WoRMS taxon details
Modiolus auriculatus Krauss, 1848
140463 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:140463)
accepted
Species
Limnoperna hepatica (A. Gould, 1850) · unaccepted (junior subjective synonym)
Modiola auriculata Krauss, 1848 · unaccepted (superseded combination)
Modiola auriculata var. aurantia Jousseaume, 1919 · unaccepted (junior subjective synonym)
Modiola cymbula Preston, 1908 · unaccepted (junior subjective synonym)
Modiola rufanensis W. H. Turton, 1932 · unaccepted (junior subjective synonym)
Modiolus agripeta Iredale, 1939 · unaccepted (junior subjective synonym)
Modiolus auriculatus var. aurantius (Jousseaume, 1919) · unaccepted (junior subjective synonym)
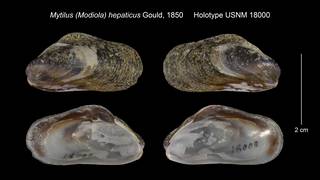
Mytilus (Modiola) hepaticus A. Gould, 1850 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Mytilus hepaticus A. Gould, 1850 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Volsella agripeta (Iredale, 1939) · unaccepted (junior subjective synonym)
- Variety Modiolus auriculatus var. aurantius (Jousseaume, 1919) accepted as Modiolus auriculatus Krauss, 1848 (junior subjective synonym)
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
(of Modiola auriculata Krauss, 1848) Krauss, F. (1848) Die Südafrikanischen Mollusken. Ein Beitrag zur Kenntniss der Mollusken des Kap- und Natallandes und zur Geographischen Verbreitung derselben mit Beschreibung und Abbildung der neuen Arten. Ebner and Seubert, Stuttgart, 140 pp., 6 pls., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/13801704
page(s): 20, pl. 2, fig. 4. [details]
page(s): 20, pl. 2, fig. 4. [details]
Type locality contained in Natal
type locality contained in Natal [from synonym] [view taxon] [details]
MolluscaBase eds. (2024). MolluscaBase. Modiolus auriculatus Krauss, 1848. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=140463 on 2024-04-19
Date
action
by
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
original description
(of Modiola auriculata Krauss, 1848) Krauss, F. (1848) Die Südafrikanischen Mollusken. Ein Beitrag zur Kenntniss der Mollusken des Kap- und Natallandes und zur Geographischen Verbreitung derselben mit Beschreibung und Abbildung der neuen Arten. Ebner and Seubert, Stuttgart, 140 pp., 6 pls., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/13801704
page(s): 20, pl. 2, fig. 4. [details]
original description (of Modiola cymbula Preston, 1908) Preston, H. B. (1908). Descriptions of new species of land, marine and freshwater shells from the Andaman Islands. <em>Records of the Indian Museum.</em> 2(2): 187-210, pls 14-17., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/35163982
page(s): 204, pl. 14, fig. 18 [details]
original description (of Modiola rufanensis W. H. Turton, 1932) Turton, W. H. (1932). The marine shells of Port Alfred S. Africa. Humphrey Milford, London. pp. i-xvi, 1-331, pls 1-70. [published 22 Dec. 1932].
page(s): 227, pl. 59, sp. 1591. [details]
original description (of Modiola auriculata var. aurantia Jousseaume, 1919) Lamy E. (1919). Les moules et les modioles de la Mer Rouge (d'après les matériaux recueillis par le Dr Jousseaume). <em>Bulletin du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle.</em> 25: 40-45, 109-114, 173-178., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/5026693
page(s): 110 [details]
original description (of Mytilus (Modiola) hepaticus A. Gould, 1850) Gould, A. A. (1850). [descriptions of new species of shells from the United States Exploring Expedition]. <em>Proceedings of the Boston Society of Natural History.</em> 3: 151-156, 169–172, 214-218, 252–256, 275–278, 292–296, 309–312, 343–348., available online at http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/8870453
page(s): 343. [details]
original description (of Modiolus agripeta Iredale, 1939) Iredale, T. (1939). Mollusca. Part I. <em>Scientific Reports of the Great Barrier Reef Expedition 1928-1929.</em> 5(6): 209-425, pls 1-7., available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/49513635
page(s): 412 [details]
context source (Introduced species) Katsanevakis, S.; Bogucarskis, K.; Gatto, F.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Deriu, I.; Cardoso A.S. (2012). Building the European Alien Species Information Network (EASIN): a novel approach for the exploration of distributed alien species data. <em>BioInvasions Records.</em> 1: 235-245., available online at http://easin.jrc.ec.europa.eu [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
context source (HKRMS) Huang ZG., Yan SK. &Zheng DQ. (1992). Biofouling communities on pier pilings in Mirs Bay. In: Morton B, editor. Proceedings of the Fourth International Marine Biological Workshop: The Marine Flora and Fauna of Hong Kong and Southern China. The marine flora and fauna of Hong Kong and southern China III. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong. 2: pp 529-543. [details]
basis of record Gofas, S.; Le Renard, J.; Bouchet, P. (2001). Mollusca. in: Costello, M.J. et al. (eds), European Register of Marine Species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. <em>Patrimoines Naturels.</em> 50: 180-213., available online at http://www.vliz.be/imisdocs/publications/ocrd/254404.pdf [details]
additional source Odhner, N. H. J. (1919). Contribution à la faune malacologique de Madagascar. <em>Arkiv för Zoologi.</em> 12(6): 1-52., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/6455070 [details]
additional source Branch, G. M. (2002). Two Oceans. 5th impression. <em>David Philip, Cate Town & Johannesburg.</em> , available online at http://books.google.es/books?id=W_2QB8ftLgcC [details]
additional source Streftaris, N., A. Zenetos & E. Papathanassiou. (2005). Globalisation in marine ecosystems: the story of non-indigenous marine species across European seas. <em>Oceanogry and Marine Biology: an Annual Review.</em> 43: 419-453. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Arnaud, P.M. (1971). Les moulières à <i>Mytilus</i> et <i>Aulacomya</i> des îles Kerguelen (Sud de l'Océan Indien). Les "moulières de seuil" et leur intérêt possible pour l'aquaculture des Pélécypodes. <em>Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, (Sér. D).</em> 272: 1423-1425. [details]
additional source Zenetos, A.; Çinar, M.E.; Pancucci-Papadopoulou, M.A.; Harmelin, J.-G.; Furnari, G.; Andaloro, F.; Bellou, N.; Streftaris, N.; Zibrowius, H. (2005). Annotated list of marine alien species in the Mediterranean with records of the worst invasive species. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 6 (2): 63-118., available online at https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273213810_Annotated_list_of_marine_alien_species_in_the_Mediterranean_with_records_of_the_worst_invasive_species [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Spencer, H.G., Marshall, B.A. & Willan, R.C. (2009). Checklist of New Zealand living Mollusca. Pp 196-219. <em>in: Gordon, D.P. (ed.) New Zealand inventory of biodiversity. Volume one. Kingdom Animalia: Radiata, Lophotrochozoa, Deuterostomia.</em> Canterbury University Press, Christchurch. [details]
additional source Kilburn, R.N. & Rippey, E. (1982) Sea Shells of Southern Africa. Macmillan South Africa, Johannesburg, xi + 249 pp.
page(s): 160. [details]
additional source Huber, M. (2010). <i>Compendium of bivalves. A full-color guide to 3,300 of the world's marine bivalves. A status on Bivalvia after 250 years of research</i>. Hackenheim: ConchBooks. 901 pp., 1 CD-ROM. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Zenetos, A.; Gofas, S.; Verlaque, M.; Cinar, M.; Garcia Raso, J.; Bianchi, C.; Morri, C.; Azzurro, E.; Bilecenoglu, M.; Froglia, C.; Siokou, I.; Violanti, D.; Sfriso, A.; San Martin, G.; Giangrande, A.; Katagan, T.; Ballesteros, E.; Ramos-Espla, A.; Mastrototaro, F.; Ocana, O.; Zingone, A.; Gambi, M.; Streftaris, N. (2010). Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2010. A contribution to the application of European Union's Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part I. Spatial distribution. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 11(2): 381-493., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.87 [details]
additional source Galil, B. (2007). Seeing Red: Alien species along the Mediterranean coast of Israel. <em>Aquatic Invasions.</em> 2(4): 281-312., available online at https://doi.org/10.3391/ai.2007.2.4.2 [details]
additional source Ozawa, H.; Sekiguchi, H. (2002). Shell Morphology of Larvae and Post-Larvae of the Two Tropical Modiolus Species, Modiolus auriculatus and Modiolus philippinarum (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). <em>Venus (Journal of the Malacological Society of Japan).</em> 61 (1-2): 25-39. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Ieyama, H. ; Kameoka, O. ; Tan, T. ; Yamasaki, J. (1994). Chromosomes and Nuclear DNA Contents of Some Species in Mytilidae. <em>VENUS (The Japanese Journals of Malacology).</em> 53(4):327-331. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
page(s): 20, pl. 2, fig. 4. [details]
original description (of Modiola cymbula Preston, 1908) Preston, H. B. (1908). Descriptions of new species of land, marine and freshwater shells from the Andaman Islands. <em>Records of the Indian Museum.</em> 2(2): 187-210, pls 14-17., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/35163982
page(s): 204, pl. 14, fig. 18 [details]
original description (of Modiola rufanensis W. H. Turton, 1932) Turton, W. H. (1932). The marine shells of Port Alfred S. Africa. Humphrey Milford, London. pp. i-xvi, 1-331, pls 1-70. [published 22 Dec. 1932].
page(s): 227, pl. 59, sp. 1591. [details]
original description (of Modiola auriculata var. aurantia Jousseaume, 1919) Lamy E. (1919). Les moules et les modioles de la Mer Rouge (d'après les matériaux recueillis par le Dr Jousseaume). <em>Bulletin du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle.</em> 25: 40-45, 109-114, 173-178., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/5026693
page(s): 110 [details]
original description (of Mytilus (Modiola) hepaticus A. Gould, 1850) Gould, A. A. (1850). [descriptions of new species of shells from the United States Exploring Expedition]. <em>Proceedings of the Boston Society of Natural History.</em> 3: 151-156, 169–172, 214-218, 252–256, 275–278, 292–296, 309–312, 343–348., available online at http://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/8870453
page(s): 343. [details]
original description (of Modiolus agripeta Iredale, 1939) Iredale, T. (1939). Mollusca. Part I. <em>Scientific Reports of the Great Barrier Reef Expedition 1928-1929.</em> 5(6): 209-425, pls 1-7., available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/49513635
page(s): 412 [details]
context source (Introduced species) Katsanevakis, S.; Bogucarskis, K.; Gatto, F.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Deriu, I.; Cardoso A.S. (2012). Building the European Alien Species Information Network (EASIN): a novel approach for the exploration of distributed alien species data. <em>BioInvasions Records.</em> 1: 235-245., available online at http://easin.jrc.ec.europa.eu [details] Available for editors
context source (HKRMS) Huang ZG., Yan SK. &Zheng DQ. (1992). Biofouling communities on pier pilings in Mirs Bay. In: Morton B, editor. Proceedings of the Fourth International Marine Biological Workshop: The Marine Flora and Fauna of Hong Kong and Southern China. The marine flora and fauna of Hong Kong and southern China III. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong. 2: pp 529-543. [details]
basis of record Gofas, S.; Le Renard, J.; Bouchet, P. (2001). Mollusca. in: Costello, M.J. et al. (eds), European Register of Marine Species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. <em>Patrimoines Naturels.</em> 50: 180-213., available online at http://www.vliz.be/imisdocs/publications/ocrd/254404.pdf [details]
additional source Odhner, N. H. J. (1919). Contribution à la faune malacologique de Madagascar. <em>Arkiv för Zoologi.</em> 12(6): 1-52., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/6455070 [details]
additional source Branch, G. M. (2002). Two Oceans. 5th impression. <em>David Philip, Cate Town & Johannesburg.</em> , available online at http://books.google.es/books?id=W_2QB8ftLgcC [details]
additional source Streftaris, N., A. Zenetos & E. Papathanassiou. (2005). Globalisation in marine ecosystems: the story of non-indigenous marine species across European seas. <em>Oceanogry and Marine Biology: an Annual Review.</em> 43: 419-453. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Arnaud, P.M. (1971). Les moulières à <i>Mytilus</i> et <i>Aulacomya</i> des îles Kerguelen (Sud de l'Océan Indien). Les "moulières de seuil" et leur intérêt possible pour l'aquaculture des Pélécypodes. <em>Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, (Sér. D).</em> 272: 1423-1425. [details]
additional source Zenetos, A.; Çinar, M.E.; Pancucci-Papadopoulou, M.A.; Harmelin, J.-G.; Furnari, G.; Andaloro, F.; Bellou, N.; Streftaris, N.; Zibrowius, H. (2005). Annotated list of marine alien species in the Mediterranean with records of the worst invasive species. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 6 (2): 63-118., available online at https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273213810_Annotated_list_of_marine_alien_species_in_the_Mediterranean_with_records_of_the_worst_invasive_species [details] Available for editors
additional source Spencer, H.G., Marshall, B.A. & Willan, R.C. (2009). Checklist of New Zealand living Mollusca. Pp 196-219. <em>in: Gordon, D.P. (ed.) New Zealand inventory of biodiversity. Volume one. Kingdom Animalia: Radiata, Lophotrochozoa, Deuterostomia.</em> Canterbury University Press, Christchurch. [details]
additional source Kilburn, R.N. & Rippey, E. (1982) Sea Shells of Southern Africa. Macmillan South Africa, Johannesburg, xi + 249 pp.
page(s): 160. [details]
additional source Huber, M. (2010). <i>Compendium of bivalves. A full-color guide to 3,300 of the world's marine bivalves. A status on Bivalvia after 250 years of research</i>. Hackenheim: ConchBooks. 901 pp., 1 CD-ROM. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Zenetos, A.; Gofas, S.; Verlaque, M.; Cinar, M.; Garcia Raso, J.; Bianchi, C.; Morri, C.; Azzurro, E.; Bilecenoglu, M.; Froglia, C.; Siokou, I.; Violanti, D.; Sfriso, A.; San Martin, G.; Giangrande, A.; Katagan, T.; Ballesteros, E.; Ramos-Espla, A.; Mastrototaro, F.; Ocana, O.; Zingone, A.; Gambi, M.; Streftaris, N. (2010). Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2010. A contribution to the application of European Union's Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part I. Spatial distribution. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 11(2): 381-493., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.87 [details]
additional source Galil, B. (2007). Seeing Red: Alien species along the Mediterranean coast of Israel. <em>Aquatic Invasions.</em> 2(4): 281-312., available online at https://doi.org/10.3391/ai.2007.2.4.2 [details]
additional source Ozawa, H.; Sekiguchi, H. (2002). Shell Morphology of Larvae and Post-Larvae of the Two Tropical Modiolus Species, Modiolus auriculatus and Modiolus philippinarum (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). <em>Venus (Journal of the Malacological Society of Japan).</em> 61 (1-2): 25-39. [details] Available for editors
additional source Ieyama, H. ; Kameoka, O. ; Tan, T. ; Yamasaki, J. (1994). Chromosomes and Nuclear DNA Contents of Some Species in Mytilidae. <em>VENUS (The Japanese Journals of Malacology).</em> 53(4):327-331. [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
Authority Brackets are not to be used around author and date if the original name is combined with an ementadion (justified or unjustified) or with an incorrect spelling of the current generic name (ICZN Art. 51.3.1). [details]From regional or thematic species database
Introduced species vector dispersal in Israeli part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Canals: natural range expansion through man-made canals [details]
To Barcode of Life (9 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (11 publications)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus BICOLORED)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus BICOLORED)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus BICOLORED)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus BLUE)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus ORANGE)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus PERIO)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus RED)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (12 nucleotides; 7 proteins)
To GenBank (12 nucleotides; 7 proteins) (from synonym Modiola auriculata Krauss, 1848)
To NMNH Extant Collection (Mytilus (Modiola) hepaticus Holotype USNM 18000) (from synonym Mytilus hepaticus A. Gould, 1850)
To PESI (from synonym Modiola auriculata Krauss, 1848)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Mollusca Collection (from synonym Mytilus hepaticus A. Gould, 1850)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Mollusca Collection
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (11 publications)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus BICOLORED)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus BICOLORED)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus BICOLORED)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus BLUE)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus ORANGE)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus PERIO)
To Conchology (Modiolus auriculatus RED)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (12 nucleotides; 7 proteins)
To GenBank (12 nucleotides; 7 proteins) (from synonym Modiola auriculata Krauss, 1848)
To NMNH Extant Collection (Mytilus (Modiola) hepaticus Holotype USNM 18000) (from synonym Mytilus hepaticus A. Gould, 1850)
To PESI (from synonym Modiola auriculata Krauss, 1848)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Mollusca Collection (from synonym Mytilus hepaticus A. Gould, 1850)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Mollusca Collection
From other sources
Hosted externally, from synonym