WoRMS taxon details
Sphyrna lewini (Griffith & Smith, 1834)
105816 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:105816)
accepted
Species
Cestracion leeuwenii Day, 1865 · unaccepted
Cestracion oceanica Garman, 1913 · unaccepted
Sphyrna diplana Springer, 1941 · unaccepted
Sphyrna leweni (Griffith & Smith, 1834) · unaccepted (misspelling)
Zygaena erythraea Klunzinger, 1871 · unaccepted
Zygaena indica van Hasselt, 1823 · unaccepted
Zygaena lewini Griffith & Smith, 1834 · unaccepted
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
Not documented
Description A coastal-pelagic, semi-oceanic shark occurring over the continental and insular shelves. Young form schools and forage...
Distribution New Jersey to Florida and the Gulf of Mexico
Description A coastal-pelagic, semi-oceanic shark occurring over the continental and insular shelves. Young form schools and forage near the bottom, migrating to deeper outer reef waters as they grow. Adults solitary or in pairs. Feeds on fishes, including other sharks and rays (Ref. 1602), cephalopods, and crustaceans; also on turtles (Ref. 2334). Non-aggressive unless stimulated by fish blood. Utilized: fresh, dried-salted, smoked and frozen; also sought for fins and hides (Ref. 9987). Game fish record weighed almost 450 kg (Ref. 9987). [details]
Distribution New Jersey to Florida and the Gulf of Mexico
Distribution New Jersey to Florida and the Gulf of Mexico [details]
Froese, R. and D. Pauly. Editors. (2024). FishBase. Sphyrna lewini (Griffith & Smith, 1834). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=105816 on 2024-04-24
Date
action
by
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 License
context source (Deepsea)
Moore, A. B.; Gates, A. R. (2015). Deep-water observation of scalloped hammerhead Sphyrna lewini in the western Indian Ocean off Tanzania. <em>Marine Biodiversity Records.</em> 8., available online at https://doi.org/10.1017/s1755267215000627 [details]
context source (HKRMS) Hong Kong marine fish database. <em>AFCD.</em> , available online at https://www.hk-fish.net/en/fish/introduction/ [details]
context source (Bermuda) Smith-Vaniz, W. F.; Collette, B. B.; Luckhurst, B. E (1999). Fishes of Bermuda: History, zoogeography, annotated checklist, and identification keys (American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists - Special Publication No.4) . ASIH, 424 pp. [details]
context source (PeRMS) Chirichigno, N.; Cornejo, M. (2001). Catálogo comentado de los peces marinos del Perú. <em>2ª ed. Instituto del Mar de Perú. Publicación Especial. Callao.</em> 314 p. [details]
basis of record van der Land, J.; Costello, M.J.; Zavodnik, D.; Santos, R.S.; Porteiro, F.M.; Bailly, N.; Eschmeyer, W.N.; Froese, R. (2001). Pisces, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 357-374 (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Castro. (1983). [details]
additional source McEachran, J. D. (2009). Fishes (Vertebrata: Pisces) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 1223–1316 in: Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas. [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Barker, A. M.; Adams, D. H.; Driggers, W. B.; Frazier, B. S.; Portnoy, D. S. (2019). Hybridization between sympatric hammerhead sharks in the western North Atlantic Ocean. <em>Biology Letters.</em> 15(4): 20190004., available online at https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2019.0004 [details]
additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source Froese, R. & D. Pauly (Editors). (2023). FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication. version (02/2023)., available online at https://www.fishbase.org [details]
context source (HKRMS) Hong Kong marine fish database. <em>AFCD.</em> , available online at https://www.hk-fish.net/en/fish/introduction/ [details]
context source (Bermuda) Smith-Vaniz, W. F.; Collette, B. B.; Luckhurst, B. E (1999). Fishes of Bermuda: History, zoogeography, annotated checklist, and identification keys (American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists - Special Publication No.4) . ASIH, 424 pp. [details]
context source (PeRMS) Chirichigno, N.; Cornejo, M. (2001). Catálogo comentado de los peces marinos del Perú. <em>2ª ed. Instituto del Mar de Perú. Publicación Especial. Callao.</em> 314 p. [details]
basis of record van der Land, J.; Costello, M.J.; Zavodnik, D.; Santos, R.S.; Porteiro, F.M.; Bailly, N.; Eschmeyer, W.N.; Froese, R. (2001). Pisces, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 357-374 (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Castro. (1983). [details]
additional source McEachran, J. D. (2009). Fishes (Vertebrata: Pisces) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 1223–1316 in: Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas. [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Barker, A. M.; Adams, D. H.; Driggers, W. B.; Frazier, B. S.; Portnoy, D. S. (2019). Hybridization between sympatric hammerhead sharks in the western North Atlantic Ocean. <em>Biology Letters.</em> 15(4): 20190004., available online at https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2019.0004 [details]
additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source Froese, R. & D. Pauly (Editors). (2023). FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication. version (02/2023)., available online at https://www.fishbase.org [details]
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From other sources
Description A coastal-pelagic, semi-oceanic shark occurring over the continental and insular shelves. Young form schools and forage near the bottom, migrating to deeper outer reef waters as they grow. Adults solitary or in pairs. Feeds on fishes, including other sharks and rays (Ref. 1602), cephalopods, and crustaceans; also on turtles (Ref. 2334). Non-aggressive unless stimulated by fish blood. Utilized: fresh, dried-salted, smoked and frozen; also sought for fins and hides (Ref. 9987). Game fish record weighed almost 450 kg (Ref. 9987). [details]Distribution New Jersey to Florida and the Gulf of Mexico [details]
Habitat nektonic [details]
| Language | Name | |
|---|---|---|
| English | scalloped hammerhead | [details] |
| German | gekerbter HammerhaiBogenstirn-Hammerhai | [details] |
| Japanese | アカシュモクザメ | [details] |
| Lithuanian | bronzinis kūjaryklis | [details] |
| Polish | głowomłot tropikalny | [details] |
| Russian | бронзовая акула-молот | [details] |
| Spanish | tiburón martillocornuda común | [details] |
| Turkish | çekiç balığı | [details] |
| Ukrainian | Бронзова риба-молотАкула-молот бронзова | [details] |
To Barcode of Life (790 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (14 publications) (from synonym Sphyrna diplana Springer, 1941)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (2 publications) (from synonym Cestracion leeuwenii Day, 1865)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (3 publications) (from synonym Cestracion oceanica Garman, 1913)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (48 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (6 publications) (from synonym Zygaena lewini Griffith & Smith, 1834)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Zygaena indica van Hasselt, 1823)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications) (from synonym Zygaena erythraea Klunzinger, 1871)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL) (from synonym Zygaena lewini Griffith & Smith, 1834)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To FishBase (from synonym Sphyrna diplana Springer, 1941)
To FishBase (from synonym Cestracion oceanica Garman, 1913)
To FishBase
To FishBase (from synonym Sphyrna leweni (Griffith & Smith, 1834))
To FishBase (from synonym Zygaena indica van Hasselt, 1823)
To FishBase (from synonym Zygaena lewini Griffith & Smith, 1834)
To FishBase (from synonym Cestracion leeuwenii Day, 1865)
To FishBase (from synonym Zygaena erythraea Klunzinger, 1871)
To FishBase images (Sphyrna lewini, Hawaii, by Randall, J.E.)
To GenBank (1369 nucleotides; 827 proteins)
To GenBank (1369 nucleotides; 827 proteins) (from synonym Zygaena lewini Griffith & Smith, 1834)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To IUCN Red List (Critically Endangered)
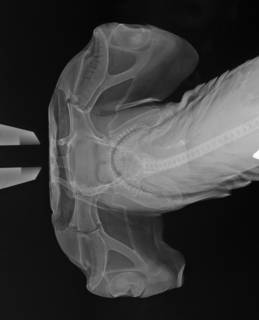
To NMNH Extant Collection (Cestracion oceanica USNM 153587 syntype radiograph caudal area) (from synonym Cestracion oceanica Garman, 1913)
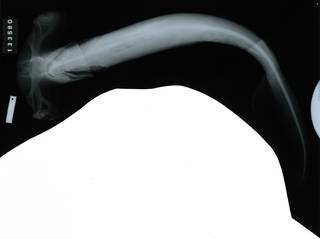
To NMNH Extant Collection (Sphyrna lewini P05265 illustration) (from synonym Sphyrna diplana Springer, 1941)
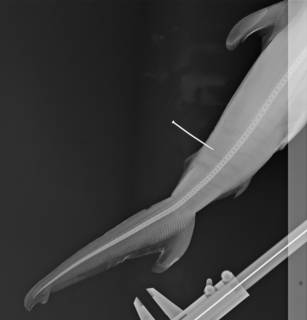
To NMNH Extant Collection (Sphyrna lewini RAD100011-001)
To NMNH Extant Collection (Sphyrna lewini RAD100011-001)
To PESI
To ITIS
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (14 publications) (from synonym Sphyrna diplana Springer, 1941)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (2 publications) (from synonym Cestracion leeuwenii Day, 1865)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (3 publications) (from synonym Cestracion oceanica Garman, 1913)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (48 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (6 publications) (from synonym Zygaena lewini Griffith & Smith, 1834)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Zygaena indica van Hasselt, 1823)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications) (from synonym Zygaena erythraea Klunzinger, 1871)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL) (from synonym Zygaena lewini Griffith & Smith, 1834)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To FishBase (from synonym Sphyrna diplana Springer, 1941)
To FishBase (from synonym Cestracion oceanica Garman, 1913)
To FishBase
To FishBase (from synonym Sphyrna leweni (Griffith & Smith, 1834))
To FishBase (from synonym Zygaena indica van Hasselt, 1823)
To FishBase (from synonym Zygaena lewini Griffith & Smith, 1834)
To FishBase (from synonym Cestracion leeuwenii Day, 1865)
To FishBase (from synonym Zygaena erythraea Klunzinger, 1871)
To FishBase images (Sphyrna lewini, Hawaii, by Randall, J.E.)
To GenBank (1369 nucleotides; 827 proteins)
To GenBank (1369 nucleotides; 827 proteins) (from synonym Zygaena lewini Griffith & Smith, 1834)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To IUCN Red List (Critically Endangered)
To NMNH Extant Collection (Cestracion oceanica USNM 153587 syntype radiograph caudal area) (from synonym Cestracion oceanica Garman, 1913)
To NMNH Extant Collection (Sphyrna lewini P05265 illustration) (from synonym Sphyrna diplana Springer, 1941)
To NMNH Extant Collection (Sphyrna lewini RAD100011-001)
To NMNH Extant Collection (Sphyrna lewini RAD100011-001)
To PESI
To ITIS