| Introduction | | Search taxa | | Taxon tree | | Taxon match | | Checklist | | Literature | | Stats | | Photogallery | | OBIS Vocab | | Log in |
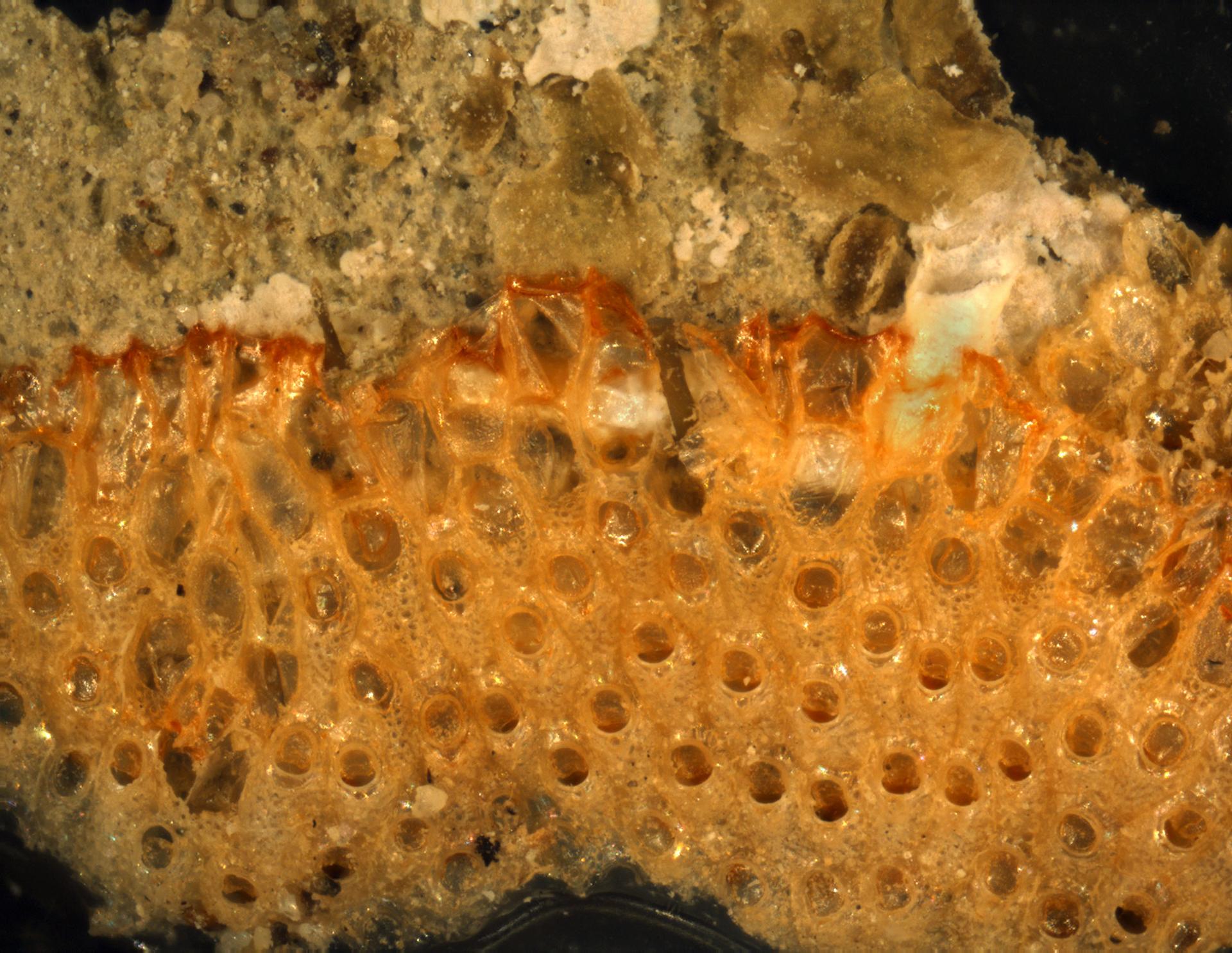
CaRMS taxon detailsCryptosula pallasiana (Moll, 1803)
111343 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:111343)
accepted
Species
Cribrilina pallasiana Moll, 1803 · unaccepted
marine,
(of ) Moll, J. P. C. (1803). Eschara, ex zoophytorum, seu, phytozoorum ordine pulcherrimum ac notatu dignissimum genus, novis speciebus auctum, methodice descriptum et iconibus ad naturam delineatis illustratum. <em>Camesiniana, Vindobonae.</em> pp.1-70., available online at https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uc1.c026109852&view=1up&seq=2 [details]
Distribution Nova Scotia to Florida
Distribution Nova Scotia to Florida [details]
Bock, P. (2021). World List of Bryozoa. Cryptosula pallasiana (Moll, 1803). Accessed through: Nozères, C., Kennedy, M.K. (Eds.) (2021) Canadian Register of Marine Species at: https://marinespecies.org/carms./aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=111343 on 2024-04-19
Nozères, C., Kennedy, M.K. (Eds.) (2024). Canadian Register of Marine Species. Cryptosula pallasiana (Moll, 1803). Accessed at: https://marinespecies.org/carms/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=111343 on 2024-04-19
original description
(of ) Moll, J. P. C. (1803). Eschara, ex zoophytorum, seu, phytozoorum ordine pulcherrimum ac notatu dignissimum genus, novis speciebus auctum, methodice descriptum et iconibus ad naturam delineatis illustratum. <em>Camesiniana, Vindobonae.</em> pp.1-70., available online at https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uc1.c026109852&view=1up&seq=2 [details]
context source (Introduced species) Fofonoff, P.W.; Ruiz, G.M.; Steves, B.; Carlton, J.T. (2014). National Exotic Marine and Estuarine Species Information System (NEMESIS), available online at http://invasions.si.edu/nemesis [details] basis of record Hayward, P.J. (2001). Bryozoa, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 325-333 (look up in IMIS) [details] additional source Gosner, K. L. (1971). Guide to identification of marine and estuarine invertebrates: Cape Hatteras to the Bay of Fundy. <em>John Wiley & Sons, Inc., London.</em> 693 pp. [pdf copepod and branchiuran :445-455]. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors additional source Linkletter, L. E. (1977). A checklist of marine fauna and flora of the Bay of Fundy. <em>Huntsman Marine Laboratory, St. Andrews, N.B.</em> 68: p. [details] additional source Meinkoth, N. A. (1981). Field guide to North American seashore creatures. <em>The Audubon Society.</em> 1-799. [details] additional source Pollock, L.W. (1998). A practical guide to the marine animals of northeastern North America. Rutgers University Press. New Brunswick, New Jersey & London. 367 pp., available online at http://books.google.com/books?id=i1AmT31cuR4C [details] additional source Muller, Y. (2004). Faune et flore du littoral du Nord, du Pas-de-Calais et de la Belgique: inventaire. [Coastal fauna and flora of the Nord, Pas-de-Calais and Belgium: inventory]. <em>Commission Régionale de Biologie Région Nord Pas-de-Calais: France.</em> 307 pp., available online at http://www.vliz.be/imisdocs/publications/145561.pdf [details] additional source Gordon, D. P.; Taylor, P. D.; Bigey, F. P. (2009). Phylum Bryozoa: moss animals, sea mats, lace corals. <em>in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2009). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 1. Kingdom Animalia: Radiata, Lophotrochozoa, Deuterostomia.</em> pp. 271-297. [details] additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors additional source Hayward, P.J. & J.S. Ryland (Eds.). (1990). The marine fauna of the British Isles and North-West Europe: 1. Introduction and protozoans to arthropods. <em>Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK.</em> 627 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details] new combination reference Canu, F.; Bassler, R. S. (1925). Les bryozoaires du Maroc et de Mauritanie (1er Mémoire). <em>Mém. Soc. Sc. Nat. du Maroc.</em> 10: 1-79. page(s): 33 [details] Available for editors  Present Present  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
From regional or thematic species database
Diet Small microorganisms, including diatoms and other unicellular algae. [details]Introduced species impact in Australian Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) : Outcompetes native species for resources and/or space [details] Introduced species impact in Australian Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) : Water abstraction or nuisance fouling [details] Introduced species remark In Mexico (Nation) : There are no specific economic or ecological impacts reported for this bryozoan. [details] Introduced species remark In Argentina (Nation) : There are no specific economic or ecological impacts reported for this bryozoan. [details] Introduced species remark In Australian Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) : There are no specific economic or ecological impacts reported for this bryozoan. [details] Introduced species remark In Brazil (Nation) : There are no specific economic or ecological impacts reported for this bryozoan. [details] Introduced species remark In Canadian Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) : There are no specific economic or ecological impacts reported for this bryozoan. [details] Introduced species remark In New Zealand (Nation) : There are no specific economic or ecological impacts reported for this bryozoan. [details] Introduced species remark In South Africa (Nation) : There are no specific economic or ecological impacts reported for this bryozoan. [details] Introduced species remark In South Atlantic Ocean (IHO Sea Area) : There are no specific economic or ecological impacts reported for this bryozoan. [details] Introduced species remark In Uruguay (Nation) : There are no specific economic or ecological impacts reported for this bryozoan. [details] Introduced species vector dispersal United States part of the North Pacific Ocean (Marine Region) Aquaculture: accidental [details] Introduced species vector dispersal in Australian Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) : Fisheries: accidental with deliberate translocations of fish or shellfish [details] Introduced species vector dispersal Argentinean part of the South Atlantic Ocean (Marine Region) Ships: accidental as attached or free-living fouling organisms [details] Introduced species vector dispersal Hawaiian part of the North Pacific Ocean (Marine Region Debris: transport of species on human generated debris (metal cylinder) [details] From other sources
Distribution Nova Scotia to Florida [details]Habitat sessile, colonial on hard substratum epifauna in the marine environment [details] Predators grazing organisms such as sea urchins and fish; also subject to competition and overgrowth from sponges, algae, and tunicates [details] Reproduction sexual and asexual; bryozoan colonies consist of replicated series of zooids, each budded asexually from a predecessor. The founding zooid metamorphoses from the sexually produced larva. Hermaphroditic. [details]
To Barcode of Life (9 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (31 publications) To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) To GenBank (4483 nucleotides; 4 proteins) To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI) To PESI To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Bryozoa Collection (2 records) To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 089437) To ITIS |