| Home | | Literature | | Log in |
| Diatoms | | Haptophytes | | Dinoflagellates | | Raphidophyceans | | Dictyochophyceans | | Pelagophyceans | | Cyanobacteria | | Greylist | | Harmful non-toxic |
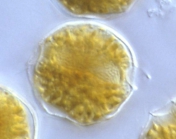
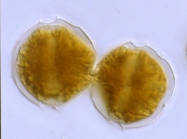
WoRMS name detailsAlexandrium fundyense Balech, 1985
156513 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:156513)
unaccepted (name rejected; "catenella" has nomenclatural priority)
Species
marine
recent only
Balech, E. (1985). The genus <i>Alexandrium</i> or <i>Gonyaulax</i> of the <i>tamarensis</i> group. In: D.M. Anderson, A.W. White and D.G. Baden (Eds.) Toxic Dinoflagellates. New York: Elsevier. P. 33–38. [details] Available for editors
Type locality contained in Fundy Bay
type locality contained in Fundy Bay [details]
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:52024
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:52024 [details] Distribution cold water; Bay of Fundy, Canada to New York.
Distribution cold water; Bay of Fundy, Canada to New York. [details]
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2024). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Alexandrium fundyense Balech, 1985. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=156513 on 2024-12-22
Date action by Copyright notice: the information originating from AlgaeBase may not be downloaded or replicated by any means, without the written permission of the copyright owner (generally AlgaeBase). Fair usage of data in scientific publications is permitted.
original description
Balech, E. (1985). The genus <i>Alexandrium</i> or <i>Gonyaulax</i> of the <i>tamarensis</i> group. In: D.M. Anderson, A.W. White and D.G. Baden (Eds.) Toxic Dinoflagellates. New York: Elsevier. P. 33–38. [details] Available for editors
basis of record Gómez, F. (2005). A list of free-living dinoflagellate species in the world's oceans. <em>Acta Bot. Croat.</em> 64(1): 129-212. [details] additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details] additional source Steidinger, K.A.; Tangen, K. (1997). Dinoflagellates. pp. 387-584. In: C.R. Tomas (ed.) (1997). Identifying Marine Phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780126930184500057 [details] additional source Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2024). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details] additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details] additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details] additional source Horner, R. A. (2002). A taxonomic guide to some common marine phytoplankton. <em>Biopress Ltd. Bristol.</em> 1-195. [details] additional source Martin, J. L.; LeGresley, M. M. ; Strain, P. M. (2001). Phytoplankton monitoring in the Western Isles region of the Bay of Fundy during 1997-98. <em>Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2349.</em> 4: 1-85. [details] source of synonymy Prud'homme van Reine, Willem F. (2017). Report of the Nomenclature Committee for Algae: 15. <em>Taxon.</em> 66(1): 191–192; February 2017., available online at https://doi.org/10.12705/661.16 [details] Available for editors toxicology source Anderson D.M., Kulis D.M., Sullivan J.J., & Hall S. 1990. Toxin composition variation in one isolate of the dinoflagellate <i>Alexandrium fundyense</i>. Toxicon 28: 885-893. [details] toxicology source Taroncher-Oldenburg G., Kulis D.M. & Anderson D.M. 1997. Toxin variability during the cell cycle of the dinoflagellate <i>Alexandrium fundyense</i>. Limnol. Oceanogr. 42: 1178 - 1188. [details]  Present Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:52024 [details]From regional or thematic species database
Harmful effect Producer of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins [details]Identification For the taxonomic circumscription of this species, see under A. carenella [details] Unreviewed
Diet general for group: both heterotrophic (eat other organisms) and autotrophic (photosynthetic) [details]Distribution cold water; Bay of Fundy, Canada to New York. [details] Habitat pelagic [details] Importance General: known for producing dangerous toxins, particularly when in large numbers, called "red tides" because the cells are so abundant they make water change color. Also they can produce non-fatal or fatal amounts of toxins in predators (particularly shellfish) that may be eaten by humans. [details] Predators marine microorganisms and animal larvae [details] Reproduction general for group: both sexual and asexual [details] |