WoRMS taxon details
Montipora verrucosa (Lamarck, 1816)
207146 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:207146)
accepted
Species
Agaricia papillosa Lamarck, 1816 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Manopora papillosa (Lamarck, 1816) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Manopora planiuscula Dana, 1846 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Manopora verrucosa (Lamarck, 1816) · unaccepted > superseded combination
Montipora ambigua Bernard, 1897 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Montipora papillosa (Lamarck, 1816) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Montipora planiuscula (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Montipora verrucosa var. angulosa Klunzinger, 1879 · unaccepted (synonymy)
Montipora verrucosa var. compacta Ortmann, 1892 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Porites verrucosa Lamarck, 1816 · unaccepted > superseded combination (basionym)
- Variety Montipora verrucosa var. angulosa Klunzinger, 1879 accepted as Montipora verrucosa (Lamarck, 1816) (synonymy)
- Variety Montipora verrucosa var. compacta Ortmann, 1892 accepted as Montipora verrucosa (Lamarck, 1816) (unaccepted > junior subjective synonym)
marine, fresh, terrestrial
(of Porites verrucosa Lamarck, 1816) Lamarck, J.-B. M. de. (1816). Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres. Tome second. <em>Paris. Verdière.</em> Vol. 2 pp. 1-568., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/47698 [details] 
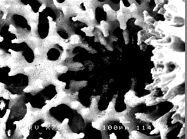
Description Thick encrusting sheets or low massive forms, sometimes with leafy edges to the colony. This species has regular shaped,...
Description Thick encrusting sheets or low massive forms, sometimes with leafy edges to the colony. This species has regular shaped, rounded tuberculae up to 0.6 cm across. This coral is similar to M. danae, but the tuberculae are smaller, more regular and rounded. Calices lie between the tuberculae as in M. danae, but are deeper. It is common on reef slopes from 5 to 25 m deep (Sheppard, 1998).
Colonies are submassive or plate-like with the surface uniformly covered with tuberculae, like those of M.dDanae. Corallites are immersed between tuberculae. Colour: blue or brown, uniform or mottled. Bright-blue or green polyps are extended during the day. Abundance: common on upper reef slopes or lagoons (Veron, 1986).
Tropical Indo-Pacific in Kalk (1958). [details]
Colonies are submassive or plate-like with the surface uniformly covered with tuberculae, like those of M.dDanae. Corallites are immersed between tuberculae. Colour: blue or brown, uniform or mottled. Bright-blue or green polyps are extended during the day. Abundance: common on upper reef slopes or lagoons (Veron, 1986).
Tropical Indo-Pacific in Kalk (1958). [details]
Hoeksema, B. W.; Cairns, S. (2024). World List of Scleractinia. Montipora verrucosa (Lamarck, 1816). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=207146 on 2024-04-24
Date
action
by
2000-09-13 07:19:12Z
changed
Garcia, Maria
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
original description
(of Montipora ambigua Bernard, 1897) Bernard H (1897). The genus Montipora, The genus Anacropora. Catalogue of the Madreporarian Corals in the British Museum (Natural History) 3: 1-192, pls. 1-33. [details]
original description (of Porites verrucosa Lamarck, 1816) Lamarck, J.-B. M. de. (1816). Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres. Tome second. <em>Paris. Verdière.</em> Vol. 2 pp. 1-568., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/47698 [details]
original description (of Manopora planiuscula Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm [details]
original description (of Montipora verrucosa var. compacta Ortmann, 1892) Ortmann, A. (1892). Die Koralriffe von Dar-es-Salaam un Umgegend. <em>Zoologische Jahrbüchern, Abteilung für Systematik, Biologie und Biogeographie der Tiere.</em> 6: 631-670, pl. 29. [details]
original description (of Agaricia papillosa Lamarck, 1816) Lamarck, J.-B. M. de. (1816). Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres, <b>Tome troisième</b> [in full: Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres présentant les caractéres généraux et particuliers de ces animaux, leur distribution, leurs classes, leurs familles, leurs genres, et la citation des principales espèces qui s'y rapportent]. <em>[book series].</em> 586 pp. Paris: Deterville/Verdière., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/47702 [details]
original description (of Montipora verrucosa var. angulosa Klunzinger, 1879) Klunzinger CB. (1879). Die Korallthiere des Rothen Meeres, 2. Theil: Die Steinkorallen. Erster Abschnitt: Die Madreporaceen und Oculinaceen. <em>Gutmann, Berlin.</em> pp. 1-88, pls. 1-10. [details]
context source (Hexacorallia) Fautin, Daphne G. (2013). Hexacorallians of the World. (look up in IMIS) [details]
basis of record Veron JEN. (1986). Corals of Australia and the Indo-Pacific. <em>Angus & Robertson Publishers.</em> [details]
additional source Boschma H. (1954). On some specimens of the coral Montipora verrucosa (Lamarck) from the Hawaiian Islands, formerly described as separate species. <em>Proceedings of the Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen - Amsterdam, Series C.</em> 57 (2): 151-158, pls. 1-3. [details]
additional source Reed, S.A., 1971. Some common Coelenterates in Kaneohe Bay, Oahu, Hawaii. In: H.M. Lenhoff, L. Muscatine & L.V. Davis, eds, Experimental Coelenterate Biology : 37-51.
page(s): 49 [details]
additional source Vaughan TW. (1918). Some shallow-water corals from Murray Island (Australia), Cocos-Keeling Island, and Fanning Island. <em>Papers from the Department of Marine Biology of the Carnegie Institution of Washington.</em> 9 (213): 49-234, pls. 20-93. [details]
additional source Trench, R.K. & R.J. Blank. (1987). Symbiodinium microadriaticum Freudenthal, S. goreauii sp. nov., S. kawagutii sp. nov. and S. pilosum sp. nov.: gymnodinioid dinoflagellate symbionts of marine invertebrates. <em>J. Phycol.</em> 23: 469-481.
page(s): 469, 470, 471, 472, 474, 476 [details]
additional source Quelch JJ. (1886). Report on the Reef-corals collected by H.M.S. 'Challenger' during the years 1873-76. <em>Report on the Scientific Results of the Voyage of H.M.S. Challenger during the years 1873–1876. Zoology.</em> 16 (46): 1-203, pl. 1-12., available online at http://www.19thcenturyscience.org/HMSC/HMSC-Reports/Zool-46/README.htm
page(s): 15, 19, 29, 30, 171, 176-177, 200 [details]
additional source Cairns, S.D., B.W. Hoeksema & J. van der Land. (1999). Appendix: List of extant stony corals. <em>Atoll Research Bulletin.</em> 459: 13-46.
page(s): 18 [details]
additional source Randall RH. (2003). An annotated checklist of hydrozoan and scleractinian corals collected from Guam and other Mariana Islands. <em>Micronesica.</em> 35-36: 121-137.
page(s): 129 [details]
additional source Cairns, S.D., B.W. Hoeksema & J. van der Land. (2007). as a contribution to UNESCO-IOC Register of Marine Organisms. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Veron JEN. (2000). Corals of the World. Vol. 1–3. <em>Australian Institute of Marine Science and CRR, Queensland, Australia.</em> [details]
additional source Veron JEN. (2002). New species described in Corals of the World. <em>Australian Institute of Marine Science Monograph Series.</em> 11: 1-209.
page(s): 18 [details]
additional source Wells JW. (1961). Notes on Indo-Pacific scleractinian corals. Part 3, A new reef coral from New Caledonia. <em>Pacific Science.</em> 15: 189-191.
page(s): 189 [details]
additional source Scheer G, Pillai CSG. (1974). Report on Scleractinia from the Nicobar Islands. <em>Zoologica, Stuttgart.</em> 42(122): 1-75.
page(s): 26 [details]
additional source Vaughan TW. (1907). Recent Madreporaria of the Hawaiian Islands and Laysan. <em>US National Museum Bulletin.</em> 59 (9): 1-427.
page(s): 8, 18, 22, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 158, 159, 160-163, 165, 167, 423, 427 Plates LIII, LIV, LV, LVI, LVII, LVIII, LIX [details]
additional source Yabe H, Sugiyama T. (1935). Revised list of the reef-corals from the Japanese seas and of the fossil reef corals of the raised reefs and the Ryukyu limestone of Japan. <em>Journal of the Geological Society of Japan.</em> 42: 379-403.
page(s): 399 [details]
additional source Nemenzo, F. (1967). Systematic studies on Philippine shallow-water scleractinians. VI Suborder Astrocoeniina (Montipora and Acropora). (Part I - Text; Part II - Plates). <em>Natural and Applied Science Bulletin, University of the Philippines.</em> 20: 1-141, 143-223.
page(s): 2, 18, 19, 152 [details]
additional source Veron JEN, Wallace CC (1984) Scleractinia of Eastern Australia – Part V. Family Acroporidae. Australian Institute of Marine Science Monograph Series 6: 1–485. [details]
additional source Crossland C (1952) Madreporaria, Hydrocorallinae, Heliopora and Tubipora. Scientific Report Great Barrier Reef Expedition 1928-29 VI(3): 85-257.
page(s): 93 [details]
additional source Gardiner JS (1898) On the perforate corals collected by the author in the South Pacific. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London 1898: 257-276, pls. 23-24. [details]
additional source Ortmann, A. (1888). Studien über Systematik und geographische Verbreitung der Steinkorallen. <em>Zoologische Jahrbücher, Abtheilung für Systematik, Biologie und Biogeographie der Tiere.</em> 3: 143-188, pl. 6.
page(s): 155, 187 [details]
additional source Milne Edwards H, Haime J (1851) Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 7. Monographie des Poritides. Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3, 16: 21-70.
page(s): 55 [details]
additional source Milne Edwards H, Haime J (1849) Mémoire sur les polypiers appartenant a aux groups naturels des zoanthaires perforés es des zoanthaires tabulés. Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des séances de l'Académie des sciences 29: 257-263.
page(s): 259 [details]
additional source Pichon, M.; Benzoni, F. (2007). Taxonomic re-appraisal of zooxanthellate Scleractinian Corals in the Maldive Archipelago. <em>Zootaxa.</em> 1441: 21–33.
page(s): 29 [details]
additional source Bedot M (1907) Madreporaires d'Amboine. Revue Suisse de Zoologie 15: 143-292, pls. 5-50.
page(s): 279-280 [details]
additional source Gravier C. (1911). Les récifs de coraux et les Madréporaires de la baie de Tadjourah (Golfe d'Aden). <em>Annales de l'Institut Océanographique de Monaco.</em> 2 (3): 1-101, pls 1-12. [details]
additional source Veron JEN, Marsh LM. (1988). Hermatypic corals of Western Australia : records and annotated species list. <em>Records Western Australian Museum Supplement.</em> 29: 1-136., available online at https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.60555
page(s): 32, 43 [details]
additional source Pillai CSG. (1972). Stony corals of the seas around India. <em>Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Corals and Coral Reefs, 1969. Marine Biological Association of India Symposium.</em> 5: 191-216.
page(s): 201 [details]
additional source Whitelegge, T. (1898). The Madroporaria of Funafuti. <em>The Australian Museum Memoir.</em> 3(6): 349-368.
page(s): 363-364 [details]
additional source Boshoff, P.H. (1981). An annotated checklist of Southern Africa Scleractinia. <em>Oceanographic Research Institute Investigational Report, Durban.</em> 49: 1-45.
page(s): 9 [details]
additional source Randall RH, Myers RF. (1983). The corals. Guide to the Coastal Resources of Guam: Vol. 2. <em>University of Guam Press, Guam, pp. 128.</em> [details]
additional source Veron, J. E. N. (2000). Corals of the World, Volume I: Family Acroporidae. Australian Institute of Marine Science. Townsville., volume 1, pp. 463.
page(s): 138-139 [details]
additional source Carlos, A. A.; Baillie, B. K.; Kawachi, M.; Maruyama, T. (1999). Phylogenetic position of Symbiodinium (Dinophyceae) isolates from tridacnids (Bivalvia), cardiids (Bivalvia), a sponge (Porifera), a soft coral (Anthozoa), and a free-living strain. Journal of Phycology, 35, 1054-1062
page(s): 1054, 1055, 1057, 1058, 1060 [details]
additional source Maragos, J. E.; Kenyon, J. (2004). Rose Atoll coral data compiled from US Fish and Wildlife Service 1994, Townsend Cromwell 2002, and Sette 2004 surveys [Table 10]. UNPUBLISHED, Unpublished
page(s): 1 [details]
additional source Ortmann, A. (1892). Die Korallriffe von Dar-es-Salaam und Umgegend. <em>Zoologische Jahrbücher Abteilung für Systematik.</em> 6: 631-670., available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/10195227
page(s): 656 [details]
additional source Maragos, J. E. (1977). Order Scleractinia, Stony Corals. Dennis M. Devaney and Lucius G. Eldredge (eds.). Bishop Museum Press. Honolulu, Hawaii, pp. 84
page(s): 162, 171-172, 180-183 [details]
additional source Studer, T. (1901). Ergebnisse einer Reise nach dem Pacific (Schauinsland 1896-1897). Madreporarier von Samoa, den Sandwich-Inseln und Laysan. Zoologische Jahrbücher Abteilung für Systematik, 14, 388
page(s): 417-418, 426 [details]
additional source Wells JW. (1954). Recent corals of the Marshall Islands: Bikini and nearby atolls, part 2, oceanography (biologic). <em>U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper.</em> 260(I): 385-486.
page(s): 392, 399, 400, 438, pls. 143, 147 [details]
additional source Reed, J. K. (1985). Deepest distribution of Atlantic hermatypic corals discovered in the Bahamas. Proceedings of the Fifth International Coral Reef Congress, 6, 249-254
page(s): 253 [details]
additional source Pillai CSG. (1983). Structure and generic diversity of recent Scleractinia of India. <em>Journal of the Marine Biological Association of India.</em> 25, 1-2, 78-90.
page(s): 85 [details]
additional source Forsman, Z. H.; Concepcion, G. T.; Haverkort, R. D.; Shaw, R. W.; Maragos, J. E.; Toonen, R. J. (2010). Ecomorph or endangered coral? DNA and microstructure reveal Hawaiian species complexes: Montipora dilatata/flabellata/turgescens & M. patula/verilli. Public Library of Science One, 5, 12, 1-10
page(s): 4 [details]
additional source Kühlmann, D. H. H. (2006). Die Steinkorallensammlung im Naturhistorischen Museum in Rudolstadt (Thüringen) nebst ökologischen Bemerkungen. Rudolstädter Naturhistorische Schriften, 13, 37-113
page(s): 62, 76, 113 [details]
new combination reference Klunzinger CB. (1879). Die Korallthiere des Rothen Meeres, 2. Theil: Die Steinkorallen. Erster Abschnitt: Die Madreporaceen und Oculinaceen. <em>Gutmann, Berlin.</em> pp. 1-88, pls. 1-10. [details]
original description (of Porites verrucosa Lamarck, 1816) Lamarck, J.-B. M. de. (1816). Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres. Tome second. <em>Paris. Verdière.</em> Vol. 2 pp. 1-568., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/47698 [details]
original description (of Manopora planiuscula Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm [details]
original description (of Montipora verrucosa var. compacta Ortmann, 1892) Ortmann, A. (1892). Die Koralriffe von Dar-es-Salaam un Umgegend. <em>Zoologische Jahrbüchern, Abteilung für Systematik, Biologie und Biogeographie der Tiere.</em> 6: 631-670, pl. 29. [details]
original description (of Agaricia papillosa Lamarck, 1816) Lamarck, J.-B. M. de. (1816). Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres, <b>Tome troisième</b> [in full: Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres présentant les caractéres généraux et particuliers de ces animaux, leur distribution, leurs classes, leurs familles, leurs genres, et la citation des principales espèces qui s'y rapportent]. <em>[book series].</em> 586 pp. Paris: Deterville/Verdière., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/47702 [details]
original description (of Montipora verrucosa var. angulosa Klunzinger, 1879) Klunzinger CB. (1879). Die Korallthiere des Rothen Meeres, 2. Theil: Die Steinkorallen. Erster Abschnitt: Die Madreporaceen und Oculinaceen. <em>Gutmann, Berlin.</em> pp. 1-88, pls. 1-10. [details]
context source (Hexacorallia) Fautin, Daphne G. (2013). Hexacorallians of the World. (look up in IMIS) [details]
basis of record Veron JEN. (1986). Corals of Australia and the Indo-Pacific. <em>Angus & Robertson Publishers.</em> [details]
additional source Boschma H. (1954). On some specimens of the coral Montipora verrucosa (Lamarck) from the Hawaiian Islands, formerly described as separate species. <em>Proceedings of the Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen - Amsterdam, Series C.</em> 57 (2): 151-158, pls. 1-3. [details]
additional source Reed, S.A., 1971. Some common Coelenterates in Kaneohe Bay, Oahu, Hawaii. In: H.M. Lenhoff, L. Muscatine & L.V. Davis, eds, Experimental Coelenterate Biology : 37-51.
page(s): 49 [details]
additional source Vaughan TW. (1918). Some shallow-water corals from Murray Island (Australia), Cocos-Keeling Island, and Fanning Island. <em>Papers from the Department of Marine Biology of the Carnegie Institution of Washington.</em> 9 (213): 49-234, pls. 20-93. [details]
additional source Trench, R.K. & R.J. Blank. (1987). Symbiodinium microadriaticum Freudenthal, S. goreauii sp. nov., S. kawagutii sp. nov. and S. pilosum sp. nov.: gymnodinioid dinoflagellate symbionts of marine invertebrates. <em>J. Phycol.</em> 23: 469-481.
page(s): 469, 470, 471, 472, 474, 476 [details]
additional source Quelch JJ. (1886). Report on the Reef-corals collected by H.M.S. 'Challenger' during the years 1873-76. <em>Report on the Scientific Results of the Voyage of H.M.S. Challenger during the years 1873–1876. Zoology.</em> 16 (46): 1-203, pl. 1-12., available online at http://www.19thcenturyscience.org/HMSC/HMSC-Reports/Zool-46/README.htm
page(s): 15, 19, 29, 30, 171, 176-177, 200 [details]
additional source Cairns, S.D., B.W. Hoeksema & J. van der Land. (1999). Appendix: List of extant stony corals. <em>Atoll Research Bulletin.</em> 459: 13-46.
page(s): 18 [details]
additional source Randall RH. (2003). An annotated checklist of hydrozoan and scleractinian corals collected from Guam and other Mariana Islands. <em>Micronesica.</em> 35-36: 121-137.
page(s): 129 [details]
additional source Cairns, S.D., B.W. Hoeksema & J. van der Land. (2007). as a contribution to UNESCO-IOC Register of Marine Organisms. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Veron JEN. (2000). Corals of the World. Vol. 1–3. <em>Australian Institute of Marine Science and CRR, Queensland, Australia.</em> [details]
additional source Veron JEN. (2002). New species described in Corals of the World. <em>Australian Institute of Marine Science Monograph Series.</em> 11: 1-209.
page(s): 18 [details]
additional source Wells JW. (1961). Notes on Indo-Pacific scleractinian corals. Part 3, A new reef coral from New Caledonia. <em>Pacific Science.</em> 15: 189-191.
page(s): 189 [details]
additional source Scheer G, Pillai CSG. (1974). Report on Scleractinia from the Nicobar Islands. <em>Zoologica, Stuttgart.</em> 42(122): 1-75.
page(s): 26 [details]
additional source Vaughan TW. (1907). Recent Madreporaria of the Hawaiian Islands and Laysan. <em>US National Museum Bulletin.</em> 59 (9): 1-427.
page(s): 8, 18, 22, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 158, 159, 160-163, 165, 167, 423, 427 Plates LIII, LIV, LV, LVI, LVII, LVIII, LIX [details]
additional source Yabe H, Sugiyama T. (1935). Revised list of the reef-corals from the Japanese seas and of the fossil reef corals of the raised reefs and the Ryukyu limestone of Japan. <em>Journal of the Geological Society of Japan.</em> 42: 379-403.
page(s): 399 [details]
additional source Nemenzo, F. (1967). Systematic studies on Philippine shallow-water scleractinians. VI Suborder Astrocoeniina (Montipora and Acropora). (Part I - Text; Part II - Plates). <em>Natural and Applied Science Bulletin, University of the Philippines.</em> 20: 1-141, 143-223.
page(s): 2, 18, 19, 152 [details]
additional source Veron JEN, Wallace CC (1984) Scleractinia of Eastern Australia – Part V. Family Acroporidae. Australian Institute of Marine Science Monograph Series 6: 1–485. [details]
additional source Crossland C (1952) Madreporaria, Hydrocorallinae, Heliopora and Tubipora. Scientific Report Great Barrier Reef Expedition 1928-29 VI(3): 85-257.
page(s): 93 [details]
additional source Gardiner JS (1898) On the perforate corals collected by the author in the South Pacific. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London 1898: 257-276, pls. 23-24. [details]
additional source Ortmann, A. (1888). Studien über Systematik und geographische Verbreitung der Steinkorallen. <em>Zoologische Jahrbücher, Abtheilung für Systematik, Biologie und Biogeographie der Tiere.</em> 3: 143-188, pl. 6.
page(s): 155, 187 [details]
additional source Milne Edwards H, Haime J (1851) Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 7. Monographie des Poritides. Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3, 16: 21-70.
page(s): 55 [details]
additional source Milne Edwards H, Haime J (1849) Mémoire sur les polypiers appartenant a aux groups naturels des zoanthaires perforés es des zoanthaires tabulés. Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des séances de l'Académie des sciences 29: 257-263.
page(s): 259 [details]
additional source Pichon, M.; Benzoni, F. (2007). Taxonomic re-appraisal of zooxanthellate Scleractinian Corals in the Maldive Archipelago. <em>Zootaxa.</em> 1441: 21–33.
page(s): 29 [details]
additional source Bedot M (1907) Madreporaires d'Amboine. Revue Suisse de Zoologie 15: 143-292, pls. 5-50.
page(s): 279-280 [details]
additional source Gravier C. (1911). Les récifs de coraux et les Madréporaires de la baie de Tadjourah (Golfe d'Aden). <em>Annales de l'Institut Océanographique de Monaco.</em> 2 (3): 1-101, pls 1-12. [details]
additional source Veron JEN, Marsh LM. (1988). Hermatypic corals of Western Australia : records and annotated species list. <em>Records Western Australian Museum Supplement.</em> 29: 1-136., available online at https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.60555
page(s): 32, 43 [details]
additional source Pillai CSG. (1972). Stony corals of the seas around India. <em>Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Corals and Coral Reefs, 1969. Marine Biological Association of India Symposium.</em> 5: 191-216.
page(s): 201 [details]
additional source Whitelegge, T. (1898). The Madroporaria of Funafuti. <em>The Australian Museum Memoir.</em> 3(6): 349-368.
page(s): 363-364 [details]
additional source Boshoff, P.H. (1981). An annotated checklist of Southern Africa Scleractinia. <em>Oceanographic Research Institute Investigational Report, Durban.</em> 49: 1-45.
page(s): 9 [details]
additional source Randall RH, Myers RF. (1983). The corals. Guide to the Coastal Resources of Guam: Vol. 2. <em>University of Guam Press, Guam, pp. 128.</em> [details]
additional source Veron, J. E. N. (2000). Corals of the World, Volume I: Family Acroporidae. Australian Institute of Marine Science. Townsville., volume 1, pp. 463.
page(s): 138-139 [details]
additional source Carlos, A. A.; Baillie, B. K.; Kawachi, M.; Maruyama, T. (1999). Phylogenetic position of Symbiodinium (Dinophyceae) isolates from tridacnids (Bivalvia), cardiids (Bivalvia), a sponge (Porifera), a soft coral (Anthozoa), and a free-living strain. Journal of Phycology, 35, 1054-1062
page(s): 1054, 1055, 1057, 1058, 1060 [details]
additional source Maragos, J. E.; Kenyon, J. (2004). Rose Atoll coral data compiled from US Fish and Wildlife Service 1994, Townsend Cromwell 2002, and Sette 2004 surveys [Table 10]. UNPUBLISHED, Unpublished
page(s): 1 [details]
additional source Ortmann, A. (1892). Die Korallriffe von Dar-es-Salaam und Umgegend. <em>Zoologische Jahrbücher Abteilung für Systematik.</em> 6: 631-670., available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/10195227
page(s): 656 [details]
additional source Maragos, J. E. (1977). Order Scleractinia, Stony Corals. Dennis M. Devaney and Lucius G. Eldredge (eds.). Bishop Museum Press. Honolulu, Hawaii, pp. 84
page(s): 162, 171-172, 180-183 [details]
additional source Studer, T. (1901). Ergebnisse einer Reise nach dem Pacific (Schauinsland 1896-1897). Madreporarier von Samoa, den Sandwich-Inseln und Laysan. Zoologische Jahrbücher Abteilung für Systematik, 14, 388
page(s): 417-418, 426 [details]
additional source Wells JW. (1954). Recent corals of the Marshall Islands: Bikini and nearby atolls, part 2, oceanography (biologic). <em>U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper.</em> 260(I): 385-486.
page(s): 392, 399, 400, 438, pls. 143, 147 [details]
additional source Reed, J. K. (1985). Deepest distribution of Atlantic hermatypic corals discovered in the Bahamas. Proceedings of the Fifth International Coral Reef Congress, 6, 249-254
page(s): 253 [details]
additional source Pillai CSG. (1983). Structure and generic diversity of recent Scleractinia of India. <em>Journal of the Marine Biological Association of India.</em> 25, 1-2, 78-90.
page(s): 85 [details]
additional source Forsman, Z. H.; Concepcion, G. T.; Haverkort, R. D.; Shaw, R. W.; Maragos, J. E.; Toonen, R. J. (2010). Ecomorph or endangered coral? DNA and microstructure reveal Hawaiian species complexes: Montipora dilatata/flabellata/turgescens & M. patula/verilli. Public Library of Science One, 5, 12, 1-10
page(s): 4 [details]
additional source Kühlmann, D. H. H. (2006). Die Steinkorallensammlung im Naturhistorischen Museum in Rudolstadt (Thüringen) nebst ökologischen Bemerkungen. Rudolstädter Naturhistorische Schriften, 13, 37-113
page(s): 62, 76, 113 [details]
new combination reference Klunzinger CB. (1879). Die Korallthiere des Rothen Meeres, 2. Theil: Die Steinkorallen. Erster Abschnitt: Die Madreporaceen und Oculinaceen. <em>Gutmann, Berlin.</em> pp. 1-88, pls. 1-10. [details]
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
Lectotype MNHN 261g [details]
Nontype (of Montipora papillosa (Lamarck, 1816)) BMNH, geounit Vietnamese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype MSI C-1105, geounit Philippines Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype MSI C-343 [details]
Nontype MSI C-908, geounit Philippines Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype NMSR 8530, geounit Eritrean Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 232-83, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 485-80, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 486-78, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 499-50, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 556-81, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 622-86, geounit Ashmore-Cartier Is. [details]
Nontype WAM 683-86, geounit Ashmore-Cartier Is. [details]
Nontype WAM 814-85, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Unknown type WAM 250-83, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
From editor or global species database
Type locality Tonga [details]From other sources
Biology zooxanthellate [details]Description Thick encrusting sheets or low massive forms, sometimes with leafy edges to the colony. This species has regular shaped, rounded tuberculae up to 0.6 cm across. This coral is similar to M. danae, but the tuberculae are smaller, more regular and rounded. Calices lie between the tuberculae as in M. danae, but are deeper. It is common on reef slopes from 5 to 25 m deep (Sheppard, 1998).
Colonies are submassive or plate-like with the surface uniformly covered with tuberculae, like those of M.dDanae. Corallites are immersed between tuberculae. Colour: blue or brown, uniform or mottled. Bright-blue or green polyps are extended during the day. Abundance: common on upper reef slopes or lagoons (Veron, 1986).
Tropical Indo-Pacific in Kalk (1958). [details]
Type locality unrecorded (Veron, 1986).
Quoy & Gaimard as authors in Kalk (1958). [details]
To Barcode of Life (1 barcode)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (5 publications) (from synonym Montipora planiuscula (Dana, 1846))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (51 publications)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (13 nucleotides; 0 proteins) (from synonym Porites verrucosa Lamarck, 1816)
To GenBank (13 nucleotides; 0 proteins)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To IUCN Red List (Least Concern)
To NMNH Extant Collection (IZCOE311verycloseup) (from synonym Manopora planiuscula Dana, 1846)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (1 record) (from synonym Manopora planiuscula Dana, 1846)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (146 records)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (2 records) (from synonym Montipora ambigua Bernard, 1897)
To ITIS
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (5 publications) (from synonym Montipora planiuscula (Dana, 1846))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (51 publications)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA)
To GenBank (13 nucleotides; 0 proteins) (from synonym Porites verrucosa Lamarck, 1816)
To GenBank (13 nucleotides; 0 proteins)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To IUCN Red List (Least Concern)
To NMNH Extant Collection (IZCOE311verycloseup) (from synonym Manopora planiuscula Dana, 1846)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (1 record) (from synonym Manopora planiuscula Dana, 1846)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (146 records)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (2 records) (from synonym Montipora ambigua Bernard, 1897)
To ITIS