| Intro | | Search taxa | | Browse taxa | | Distributions | | Terminology | | References | | Statistics | | Online sources | | Tutorial | | Log in |
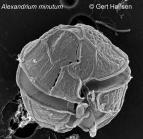
Traits taxon detailsAlexandrium minutum Halim, 1960
109711 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:109711)
accepted
Species
marine,
Halim Y. (1960). Alexandrium minutum, n. gen. n. sp. dinoflagellé provocant des “eaux rouges”. <em>Vie et Milieu.</em> 11: 102-105. [details] Available for editors
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Alexandrium minutum Halim, 1960. Accessed through: Marine Species Traits editorial board (2025) Marine Species Traits at: https://marinespecies.org/traits/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=109711 on 2025-04-26
Marine Species Traits editorial board (2025). Marine Species Traits. Alexandrium minutum Halim, 1960. Accessed at: https://www.marinespecies.org/traits/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=109711 on 2025-04-26
Date action by 2015-06-26 12:00:51Z changed db_admin
original description
Halim Y. (1960). Alexandrium minutum, n. gen. n. sp. dinoflagellé provocant des “eaux rouges”. <em>Vie et Milieu.</em> 11: 102-105. [details] Available for editors
basis of record Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details] additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details] additional source Ignatiades, L.; Gotsis-Skretas, O.; Metaxatos, A. (2007). Field and culture studies on the ecophysiology of the toxic dinoflagellate <i>Alexandrium minutum</i> (Halim) present in Greek coastal waters. <em>Harmful Algae.</em> 6(2): 153-165., available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2006.04.002 [details] additional source Hallegraeff G.M., Steffensen D.A. & Wetherbee R. 1988. Three estuarine Australian dinoflagellates that can produce paralytic shellfish toxins. J. Plankton Res. 10: 533-541. [details] additional source Balech, E. 1995. The Genus <i>Alexandrium</i> Halim (Dinoflagellata). Sherkin Island Marine Station, Sherkin Island, Co. Cork, Ireland, 151. [details] Available for editors additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details] additional source Chang, F.H.; Charleston, W.A.G.; McKenna, P.B.; Clowes, C.D.; Wilson, G.J.; Broady, P.A. (2012). Phylum Myzozoa: dinoflagellates, perkinsids, ellobiopsids, sporozoans, in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2012). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 3. Kingdoms Bacteria, Protozoa, Chromista, Plantae, Fungi. pp. 175-216. [details] redescription Balech, E. (1989). Redescription of Alexandrium minutum Halim (Dinophyceae) type species of the genus Alexandrium. <em>Phycologia.</em> 28(2), 206–211. [details] Available for editors toxicology source Oshima Y., Hirota M., Yasumoto T., Hallegraeff G.M., Blackburn S.I. & Steffensen D.A. 1989. Production of paralytic shellfish toxins by the dinoflagellate <i>Alexandrium minutum</i> Halim from Australia. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 55: 925. [details] toxicology source Franco J.M., Fernandez P. & Reguera B. 1994. Toxin profiles of natural population and cultures of <i>Alexandrium minutum</i> Halim from Galician (Spain) coastal waters. J. Appl. Phycol. 6: 275-279.<br><br> [details] toxicology source Chang F.H., Anderson D.M., Kulis D.M. & Till D.G. 1997. Toxin production of <i>Alexandrium minutum</i> (Dinophyceae) from the Bay of Plenty, New Zealand. Toxicon 35: 393-409. [details] ecology source Leles, S. G.; Mitra, A.; Flynn, K. J.; Tillmann, U.; Stoecker, D.; Jeong, H. J.; Burkholder, J.; Hansen, P. J.; Caron, D. A.; Glibert, P. M.; Hallegraeff, G.; Raven, J. A.; Sanders, R. W.; Zubkov, M. (2019). Sampling bias misrepresents the biogeographical significance of constitutive mixotrophs across global oceans. <em>Global Ecology and Biogeography.</em> 28(4): 418-428., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12853 [details] Available for editors ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details] ecology source Jeong, H.; Park, J.; Nho, J.; Park, M.; Ha, J.; Seong, K.; Jeng, C.; Seong, C.; Lee, K.; Yih, W. (2005). Feeding by red-tide dinoflagellates on the cyanobacterium Synechococcus. <em>Aquatic Microbial Ecology.</em> 41: 131-143., available online at https://doi.org/10.3354/ame041131 [details]  Present Present  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
Published in AlgaeBase
 To Barcode of Life (6 barcodes) To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) To Dyntaxa To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Alexandrium minutum) To GenBank (87084 nucleotides; 17093 proteins) To Global Invasive Species Database (GISD) To Information system on Aquatic Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species (AquaNIS) To PESI To ITIS |