| Intro | | Search taxa | | Browse taxa | | Distributions | | Terminology | | References | | Statistics | | Online sources | | Tutorial | | Log in |
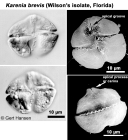
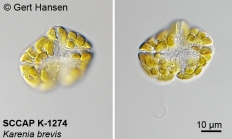
WRiMS taxon detailsKarenia brevis (C.C.Davis) Gert Hansen & Moestrup, 2000
233015 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:233015)
accepted
Species
Gymnodinium breve C.C.Davis, 1948 · unaccepted (basionym)
marine
(of Gymnodinium breve C.C.Davis, 1948) Davis C. C. 1948. <i>Gymnodinium brevis</i> sp. nov., a cause of discolored water and animal mortality in the Gulf of Mexico. Bot. Gaz. 109: 358-360. [details]
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Karenia brevis (C.C.Davis) Gert Hansen & Moestrup, 2000. Accessed through: Costello, M. J.; Ahyong, S.; Bieler, R.; Boudouresque, C.; Desiderato, A.; Downey, R.; Galil, B. S.; Gollasch, S.; Hutchings, P.; Kamburska, L.; Katsanevakis, S.; Kupriyanova, E.; Lejeusne, C.; Ma, K. C. K.; Marchini, A.; Occhipinti, A.; Pagad, S.; Pino, L.; Poore, G. C. B.; Rewicz, T.; Rius, M.; Robinson, T. B.; Sobczyk, R.; Stepien, A.; Turon, X.; Valls Domedel, G.; Verleye, T.; Vieira, L. M.; Willan, R. C.; Zhan, A. (2025) World Register of Introduced Marine Species (WRiMS) at: https://www.marinespecies.org/introduced/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=233015 on 2025-04-26
Costello, M. J.; Ahyong, S.; Bieler, R.; Boudouresque, C.; Desiderato, A.; Downey, R.; Galil, B. S.; Gollasch, S.; Hutchings, P.; Kamburska, L.; Katsanevakis, S.; Kupriyanova, E.; Lejeusne, C.; Ma, K. C. K.; Marchini, A.; Occhipinti, A.; Pagad, S.; Pino, L.; Poore, G. C. B.; Rewicz, T.; Rius, M.; Robinson, T. B.; Sobczyk, R.; Stępień, A.; Turon, X.; Valls Domedel, G.; Verleye, T.; Vieira, L. M.; Willan, R. C.; Zhan, A. (2025). World Register of Introduced Marine Species (WRiMS). Karenia brevis (C.C.Davis) Gert Hansen & Moestrup, 2000. Accessed at: https://marinespecies.org/introduced/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=233015 on 2025-04-26
Date action by 2006-07-26 06:43:45Z created Camba Reu, Cibran 2015-06-26 12:00:51Z changed db_admin
original description
(of Gymnodinium breve C.C.Davis, 1948) Davis C. C. 1948. <i>Gymnodinium brevis</i> sp. nov., a cause of discolored water and animal mortality in the Gulf of Mexico. Bot. Gaz. 109: 358-360. [details]
context source (HKRMS) Clark, A. M. (1982). Echinoderms of Hong Kong. <em>In: Morton B, editor. Proceedings of the first international marine biological workshop: The marine flora and fauna of Hong Kong and southern China. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong.</em> 1: 485-501. [details] basis of record Gómez, F. (2005). A list of free-living dinoflagellate species in the world's oceans. <em>Acta Bot. Croat.</em> 64(1): 129-212. [details] basis of record Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details] additional source Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details] additional source Steidinger, K. A., M. A. Faust, and D. U. Hernández-Becerril. 2009. Dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 131–154 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College [details] additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details] additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors new combination reference Daugbjerg, N.; Hansen, G.; Larsen, J.; Moestrup, O. (2000). Phylogeny of some of the major genera of dinoflagellates based on ultrastructure and partial LSU rDNA sequence data, including the erection of three new genera of unarmoured dinoflagellates. <em>Phycologia.</em> 39(4): 302-317., available online at https://doi.org/10.2216/i0031-8884-39-4-302.1 [details] toxicology source Landsberg J.H. & Steidinger K.A. 1998. A historical review of <i>Gymnodinium breve</i> red tides implicated in mass mortalities of the manatee (<i>Trichechus manatus latirostris</i>) in Florida. In: <i>Harmful Algae</i> (Ed. by B. Reguera, J. Blanco, M. L. Fernández & T. Wyatt), pp. 97-100. Xunta de Galicia and IOC, UNESCO, Santiago de Compostela. [details] ecology source Leles, S. G.; Mitra, A.; Flynn, K. J.; Tillmann, U.; Stoecker, D.; Jeong, H. J.; Burkholder, J.; Hansen, P. J.; Caron, D. A.; Glibert, P. M.; Hallegraeff, G.; Raven, J. A.; Sanders, R. W.; Zubkov, M. (2019). Sampling bias misrepresents the biogeographical significance of constitutive mixotrophs across global oceans. <em>Global Ecology and Biogeography.</em> 28(4): 418-428., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12853 [details] Available for editors ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details] ecology source Glibert, P.; Burkholder, J.; Kana, T.; Alexander, J.; Skelton, H.; Shilling, C. (2009). Grazing by Karenia brevis on Synechococcus enhances its growth rate and may help to sustain blooms. <em>Aquatic Microbial Ecology.</em> 55: 17-30., available online at https://doi.org/10.3354/ame01279 [details]  Present Present  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Gymnodinium breve C.C.Davis, 1948) (from synonym Gymnodinium breve C.C.Davis, 1948)Published in AlgaeBase  To Barcode of Life (2 barcodes) To Biodiversity Heritage Library (4 publications) To Biodiversity Heritage Library (50 publications) (from synonym Gymnodinium breve C.C.Davis, 1948) To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Karenia brevis) To GenBank (243310 nucleotides; 69210 proteins) To GenBank (243310 nucleotides; 69210 proteins) (from synonym Gymnodinium breve C.C.Davis, 1948) To PESI |