| Introduction | | Search taxa | | Taxon tree | | Specimens | | Attributes | | Literature | | Photo gallery | | Stats | | Log in |
WoRMS taxon detailsDiadema setosum (Leske, 1778)
213372 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:213372)
accepted
Species
Calmarius annellata A. Agassiz, 1872 (ex Gray, MS) · unaccepted (manuscript name appearing in a...)
manuscript name appearing in a synonymy list in Agassiz (1872-74: p. 104) Centrechinus (Diadema) setosus (Leske, 1778) · unaccepted (transferred to Diadema)
Centrechinus setosus (Leske, 1778) · unaccepted (unaccepted combination)
Centrostephanus setosum (Leske, 1778) · unaccepted (transferred to Diadema)
Centrostephanus setosus (Leske, 1778) · unaccepted (tranferred to Diadema)
Cidaris (Diadema) tenuispina Philippi, 1845 · unaccepted (subjective junior synonym)
Cidarites diadema (Gmelin, 1791) · unaccepted (subjective junior synonym)
Diadema lamarcki (Gmelin, 1791) · unaccepted (subjective junior synonym)
Diadema nudum A. Agassiz, 1864 · unaccepted (subjective junior synonym)
Diadema saxatile (Linnaeus, 1758) · unaccepted (subjective junior synonym)
Diadema setosa (Leske, 1778) · unaccepted (incorrect declination of species name)
Diadema setosum f. depressa Dollfus & Roman, 1981 · unaccepted (infrasubspecific and unavailable...)
infrasubspecific and unavailable according to ICZN 4th Ed. Article 45.6.3 Diadema turcarum Rumph, 1711 · unaccepted (pre-Linnean)
Echinometra setosa Rumphius, 1705 · unaccepted (pre-Linnean)
Echinometra setosa Leske, 1778 · unaccepted (transferred to Diadema)
Echinus saxatilis Linnaeus, 1758 · unaccepted (subjective junior synonym - but...)
subjective junior synonym - but see below in notes section Echinus ſaxatilis Linnaeus, 1758 · unaccepted (incorrect original spelling (ICZN...)
incorrect original spelling (ICZN 4th ed., Art. 32.5.)
marine,
recent only
(of Echinometra setosa Leske, 1778) Leske, N. G. 1778. Jacobi Theodori Klein naturalis dispositio echinodermatum . . ., edita et descriptionibus novisque inventis et synonomis auctorem aucta. Addimenta ad I. T. Klein naturalem dispositionem Echinodermatum. G. E. Beer, Leipzig, xxii+278 pp., available online at http://gdz.sub.uni-goettingen.de/dms/load/img/?PID=PPN573613834
page(s): 100, 104; pl. 37: figs 1-2, pl. 46: fig. 1, pl. 51: figs 1-2 [details]
Note Amboina, Moluccas. Gray considered as author...
Unreviewed
Type locality Amboina, Moluccas. Gray considered as author in Ludwig (1899).D. setosa place in family 'Centrechinidae' in Kalk (1958). According to Clark & Rowe (1971), some of the records may be interchangeable with D. savignyi. In Rowe & Gates (1995), status and whereabouts of type specimens undetermined and type locality unknown. [details]
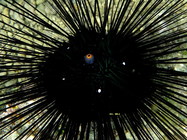
Description Colour in life: black, red ring around anus and white spot over each genital pore (Humphreys, 1981).
One specimen with...
Description Colour in life: black, red ring around anus and white spot over each genital pore (Humphreys, 1981). One specimen with eight parastic eulimid gastropods Echineulima mittrei mittrei (Petit, 1851). Also distributed in Saudi Arabia (Clark, 1954); Australia (Kalk (1958) and Rowe & Gates (1995)); SE Arabia, Persian Gulf, Ceylon, Bay of Bengal, East Indies, north Australia, Philippine, China, south Japan and South Pacific Is. (Clark & Rowe, 1971); India (Sastry, 1996). General distribution: tropical Indo-Pacific in Kalk (1958); tropical, Indo-west-central Pacific Ocean, depth range 0-70 m. (Rowe & Gates, 1995). Ecology: benthic, inshore, continental shelf (Rowe & Gates, 1995). [details]
Kroh, A.; Mooi, R. (2025). World Echinoidea Database. Diadema setosum (Leske, 1778). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=213372 on 2025-07-15
Date action by 2000-09-25 07:20:28Z changed Garcia, Maria
Nomenclatureoriginal description
(of Diadema turcarum Rumph, 1711) Rumph, G.E. (= Rumphius, G.E.). (1711). Thesaurus imaginum piscium testaceorum. Petrum vander Aa, Lugduni Batavorum. 15 pp., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/43058158 page(s): 2; pl. 14: fig. B [details] original description (of Echinometra setosa Rumphius, 1705) Rumphius, G.E. (1705). D'Amboinsche Rariteitkamer, of eene beschryvinge van allerhannde Schaalvisschen; benevens de voornaamste Hoorntjes en Schulpen, als ook zommige,mineraalen, gesteenten; enz. D'Ambonische Rariteitkamer, behelzende eene beschryviinge van allerhande zoo weeke als harade Schaalvisschen, te weete raare krabben, kreeften,en dirgelyke Zeedieren, als mede aallerbande Hoorntjes en Schulpen, die men in d'Amboinsche Zee vindt: Daar benevens zommige Mineraaalen, Gesteenten, en soorten van Aarde,die in d'Amboinsche, en zommige omleggende Eilanden gevonden worden. Verdeelt in drie Boeken, En met nodige Printverbeeldingen, alle naar't leven getekent; voorzien. Beschreven door George Everhardus Rumphius. Jan Roman de Joonge, T'Amsterdam. 381 pp. , available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/43418947 page(s): 35-36; pl. 13: fig. 5 [details] Available for editors original description (of Diadema setosum f. depressa Dollfus & Roman, 1981) Dollfus, R.-P. & Roman, J. 1981. Les Échinides de la mer Rouge. Ministère des Universités, Comité des Travaux Historiques et Scientifiques, Mémoires de la Section des Sciences 9, 1-145. page(s): 38-39; pl. 5: figs 4-6, pl. 6: figs 1-3 [details] original description (of Cidaris (Diadema) tenuispina Philippi, 1845) Philippi, R. A. 1845. Beschreibung einiger neuer Echinodermen nebst kritischen Bemerckungen über einige weniger bekannte Arten. Archiv für Naturgeschichte 11, 344-359., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/6483274 page(s): 354 [details] original description (of Diadema nudum A. Agassiz, 1864) Agassiz, A. (1864). Synopsis of the echinoids collected by Dr. W. Stimpson on the North Pacific Exploring Expedition under the command of Captains Ringgold and Rodgers. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. 15 (1863), 352-361., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/1958617 page(s): 353-Q126 [details] original description (of Echinus ſaxatilis Linnaeus, 1758) Linnaeus, C. (1758). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. [The system of nature through the three kingdoms of nature, according to classes, orders, genera, species, with characters, differences, synonyms, places.]. <em>Impensis Direct. Laurentii Salvii. Holmiae [Stockholm].</em> 1(10) [iii], 824 p., available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/726886 [details] Available for editors original description (of Echinometra setosa Leske, 1778) Leske, N. G. 1778. Jacobi Theodori Klein naturalis dispositio echinodermatum . . ., edita et descriptionibus novisque inventis et synonomis auctorem aucta. Addimenta ad I. T. Klein naturalem dispositionem Echinodermatum. G. E. Beer, Leipzig, xxii+278 pp., available online at http://gdz.sub.uni-goettingen.de/dms/load/img/?PID=PPN573613834 page(s): 100, 104; pl. 37: figs 1-2, pl. 46: fig. 1, pl. 51: figs 1-2 [details] original description (of Calmarius annellata A. Agassiz, 1872 (ex Gray, MS)) Agassiz, A. (1872-1874). Revision of the Echini. <em>Illustrated Catalogue of the Museum of Comparative Zoölogy at Harvard College.</em> vol. 7: pt. 1-2: i-xii, 1-378, pls. 1-49 (1872); pt. 3: 379-628+1, pls. 50-77 (1873); pt. 4: 629-762, pls. 78-94 (1874)., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/4327273 page(s): 104 [details] original description (of Echinus saxatilis Linnaeus, 1758) Linnaeus, C. (1758). Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. [The system of nature through the three kingdoms of nature, according to classes, orders, genera, species, with characters, differences, synonyms, places.]. <em>Impensis Direct. Laurentii Salvii. Holmiae [Stockholm].</em> 1(10) [iii], 824 p., available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/726886 page(s): 664 [details] Available for editors basis of record Clark, A. M.; Rowe, F. W. E. (1971). Monograph of shallow-water indo-west Pacific Echinoderms. <em>Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History).</em> London. x + 238 p. + 30 pls., available online at http://www.abctaxa.be/downloads/additional-information-volume-1/works-famous-holothuroid-workers/fwe-rowe/MonographIndoWestPacific.pdf [details] Ecologyecology source
Bronstein, O., Kroh, A. & Loya, Y. (2016). Reproduction of the long-spined sea urchin Diadema setosum in the Gulf of Aqaba - implications for the use of gonad-indexes. <em>Scientific Reports.</em> 6: 29569., available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29569 [details] Available for editors Othercontext source (Introduced species)
Katsanevakis, S.; Bogucarskis, K.; Gatto, F.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Deriu, I.; Cardoso A.S. (2012). Building the European Alien Species Information Network (EASIN): a novel approach for the exploration of distributed alien species data. <em>BioInvasions Records.</em> 1: 235-245., available online at http://easin.jrc.ec.europa.eu [details] Available for editors
context source (HKRMS) Lam KKY. (2001). Algal and sessile invertebrate recruitment onto an experimental PFA-concrete artificial reef in Hong Kong. In: Morton B, editor. Asian Marine Biology 17. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong. pp 55-76. [details] additional source Rowe, F. W. E.; Gates, J. (1995). Echinodermata. <em>In: Wells, A.; Houston, W.W.K. (Ed.) Zoological catalogue of Australia, 33. CSIRO: Melbourne. ISBN 0-643-05696-3. XIII.</em> 510 pp. [details] additional source Mortensen, T. (1940). A Monograph of the Echinoidea. III, 1. Aulodonta, with Additions to Vol. II (Lepidocentroida and Stirodonta). 370 pp., C. A. Reitzel, Copenhagen. page(s): 256-264 [details] additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors additional source Zenetos, A., S. Gofas, M. Verlaque, M. Cinar, J. Garcia Raso, C. Bianchi, C. Morri, E. Azzurro, M. Bilecenoglu, C. Froglia, I. Siokou, D. Violanti, A. Sfriso, G. San Martin, A. Giangrande, T. Katagan, E. Ballesteros, A. Ramos-Espla, F. Mastrototaro, O. Ocana, A. Zingone, M,. Gambi & N. Streftaris. (2010). Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2010. A contribution to the application of European Union's Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part I. Spatial distribution. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 11(2): 381-493., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.87 [details] additional source Zenetos, A., E. Meric, M. Verlaque, P. Galli, C.F. Boudouresque, A. Giangrande, M. Cinar & M. Bilecenoglu. (2008). Additions to the annotated list of marine alien biota in the Mediterranean with special emphasis on Foraminifera and Parasites. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 9(1): 119-165., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.146 [details] Available for editors additional source Zirler, R.; Schmidt, L.-M.; Roth, L.; Corsini-Foka, M.; Kalaentzis, K.; Kondylatos, G.; Mavrouleas, D.; Bardanis, E.; Bronstein, O. (2023). Mass mortality of the invasive alien echinoid <i>Diadema setosum</i> (Echinoidea: Diadematidae) in the Mediterranean Sea. <em>Royal Society Open Science.</em> 10(5)., available online at https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rsos.230251 [details]  Present Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
Introduced species impact in Lebanese part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Human health [details]Introduced species impact in Lebanese part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Other impact - undefined or uncertain [details] From regional or thematic species database
Introduced species impact in Lebanese part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Outcompetes native species for resources and/or space [details]Introduced species vector dispersal in Turkish part of the Mediterranean Sea - Eastern Basin (Marine Region) : Shipping [details] Unreviewed
Description Colour in life: black, red ring around anus and white spot over each genital pore (Humphreys, 1981).One specimen with eight parastic eulimid gastropods Echineulima mittrei mittrei (Petit, 1851). Also distributed in Saudi Arabia (Clark, 1954); Australia (Kalk (1958) and Rowe & Gates (1995)); SE Arabia, Persian Gulf, Ceylon, Bay of Bengal, East Indies, north Australia, Philippine, China, south Japan and South Pacific Is. (Clark & Rowe, 1971); India (Sastry, 1996). General distribution: tropical Indo-Pacific in Kalk (1958); tropical, Indo-west-central Pacific Ocean, depth range 0-70 m. (Rowe & Gates, 1995). Ecology: benthic, inshore, continental shelf (Rowe & Gates, 1995). [details] Type locality Amboina, Moluccas. Gray considered as author in Ludwig (1899). D. setosa place in family 'Centrechinidae' in Kalk (1958). According to Clark & Rowe (1971), some of the records may be interchangeable with D. savignyi. In Rowe & Gates (1995), status and whereabouts of type specimens undetermined and type locality unknown. [details]
To Barcode of Life (31 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (105 publications) (from synonym Echinus saxatilis Linnaeus, 1758) To Biodiversity Heritage Library (18 publications) (from synonym Centrechinus setosus (Leske, 1778)) To Biodiversity Heritage Library (183 publications) To Biodiversity Heritage Library (32 publications) (from synonym Diadema setosa (Leske, 1778)) To Biodiversity Heritage Library (42 publications) (from synonym Diadema saxatile (Linnaeus, 1758)) To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL) To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Diadema setosum) To Fishipedia To GenBank (1327 nucleotides; 1260 proteins) To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI) To MNHN Type collection (IE 2016-937) (from synonym Diadema setosum f. depressa Dollfus & Roman, 1981) To PESI (from synonym Echinus saxatilis Linnaeus, 1758) To PESI To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Echinodermata Collection (27 records) ZooBank LSID: urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:F30F5D1B-8009-443A-B914-DB0D04868BE6 (from synonym Echinus saxatilis Linnaeus, 1758) |