| Intro | | About | | Wiki | | Search traits | | Data explorer | | Literature | | Definitions | | Sources | | Webservices | | Statistics | | Feedback | | Editors | | Log in |
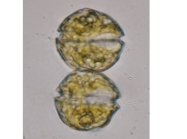
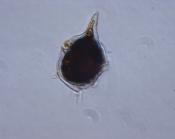
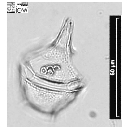
WoRMS taxon detailsAmylax triacantha (Jørgensen) Sournia, 1984
110007 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:110007)
accepted
Species
Gonyaulax hyperborea (Cleve) Paulsen, 1903 · unaccepted (synonym)
Gonyaulax triacantha Jörgensen, 1899 · unaccepted (basionym)
Gonyaulax triacantha var. subinermis Conrad, 1939 · unaccepted (following synonymy on species level)
marine
Not documented
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:47161
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:47161 [details]
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Amylax triacantha (Jørgensen) Sournia, 1984. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=110007 on 2025-04-26
Date action by 2006-07-27 06:59:07Z changed Camba Reu, Cibran 2015-06-26 12:00:51Z changed db_admin Copyright notice: the information originating from AlgaeBase may not be downloaded or replicated by any means, without the written permission of the copyright owner (generally AlgaeBase). Fair usage of data in scientific publications is permitted. Nomenclatureoriginal description
(of Gonyaulax triacantha var. subinermis Conrad, 1939) Conrad, W. (1939). Notes protoistologiques: 13. <i>Goniaulax triacantha</i> Jörg., var. nov. Subermis. <i>Bull. Mus. royal d'Hist. Nat. Belg./Med. Kon. Natuurhist. Mus. Belg. 15(57)</i>: 1-3 (look up in IMIS) [details] basis of record Gómez, F. (2005). A list of free-living dinoflagellate species in the world's oceans. <em>Acta Bot. Croat.</em> 64(1): 129-212. [details] basis of record Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details] Ecologyecology source
Koike, K.; Takishita, K. (2008). Anucleated cryptophyte vestiges in the gonyaulacalean dinoflagellates Amylax buxus and Amylax triacantha (Dinophyceae). <em>Phycological Research.</em> 56(4): 301-311., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1835.2008.00512.x [details] ecology source Leles, S. G.; Mitra, A.; Flynn, K. J.; Stoecker, D. K.; Hansen, P. J.; Calbet, A.; McManus, G. B.; Sanders, R. W.; Caron, D. A.; Not, F.; Hallegraeff, G. M.; Pitta, P.; Raven, J. A.; Johnson, M. D.; Glibert, P. M.; Våge, S. (2017). Oceanic protists with different forms of acquired phototrophy display contrasting biogeographies and abundance. <em>Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences.</em> 284(1860): 20170664., available online at https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2017.0664 [details] Available for editors ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details] ecology source Park, M. G.; Kim, M.; Kang, M. (2013). A Dinoflagellate <i>Amylax triacantha</i> with Plastids of the Cryptophyte Origin: Phylogeny, Feeding Mechanism, and Growth and Grazing Responses. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 60(4): 363-376., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12041 [details] Othercontext source (HKRMS)
Lam CWY. & Ho KC. (1988). Phytoplankton characteristics of Tolo Harbour. In: Morton B, editor. Asian Marine Biology 6. pp 5-18. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong. [details]
additional source Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details] additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details] additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details] additional source Brandt, S. (2001). Dinoflagellates, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 47-53 (look up in IMIS) [details] additional source Steidinger, K. A., M. A. Faust, and D. U. Hernández-Becerril. 2009. Dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 131–154 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College [details] additional source Steidinger, K.A.; Tangen, K. (1997). Dinoflagellates. pp. 387-584. In: C.R. Tomas (ed.) (1997). Identifying Marine Phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780126930184500057 [details]  Present Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:47161 [details]Unreviewed
Diet general for group: both heterotrophic (eat other organisms) and autotrophic (photosynthetic) [details]Habitat pelagic [details] Importance General: known for producing dangerous toxins, particularly when in large numbers, called "red tides" because the cells are so abundant they make water change color. Also they can produce non-fatal or fatal amounts of toxins in predators (particularly shellfish) that may be eaten by humans. [details] Predators marine microorganisms and animal larvae [details] Reproduction general for group: both sexual and asexual [details]
PlanktonNet Image
Published in AlgaeBase  Published in AlgaeBase  (from synonym Gonyaulax triacantha Jörgensen, 1899) (from synonym Gonyaulax triacantha Jörgensen, 1899)Published in AlgaeBase  (from synonym Gonyaulax hyperborea (Cleve) Paulsen, 1903) (from synonym Gonyaulax hyperborea (Cleve) Paulsen, 1903)To Biodiversity Heritage Library (33 publications) (from synonym Gonyaulax triacantha Jörgensen, 1899) To Dyntaxa To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Amylax triacantha) To GenBank (5 nucleotides; 0 proteins) To GenBank (5 nucleotides; 0 proteins) (from synonym Gonyaulax triacantha Jörgensen, 1899) To PESI To ITIS |