| About | | Search taxa | | Taxon tree | | Search literature | | Checklist | | Stats | | Log in |
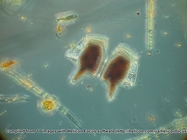
ERMS taxon detailsDinophysis caudata Saville-Kent, 1881
109612 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:109612)
accepted
Species
Dinophysis diegensis Kofoid, 1907 · unaccepted (synonym)
marine, brackish,
Saville-Kent W. 1880/82. A manual of the infusoria. London, Bogue 1: 460-461. [details]
Kent, W.S. (1880-1881). A manual of the infusoria, including a description of all known flagellate, ciliate, and tentaculiferous protozoa, British and foreign and an account of the organization and affinities of the sponges. Vol. I pp. 289-720. London., available online at https://archive.org/details/manualofinfusori18081kent [details]
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2024). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Dinophysis caudata Saville-Kent, 1881. Accessed through: Costello, M.J.; Bouchet, P.; Boxshall, G.; Arvanitidis, C.; Appeltans, W. (2024) European Register of Marine Species at: http://marbef.org/data/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=109612 on 2024-05-17
Costello, M.J.; Bouchet, P.; Boxshall, G.; Arvanitidis, C.; Appeltans, W. (2024). European Register of Marine Species. Dinophysis caudata Saville-Kent, 1881. Accessed at: http://www.marbef.org/data/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=109612 on 2024-05-17
Date action by 2004-12-21 15:54:05Z created db_admin Copyright notice: the information originating from AlgaeBase may not be downloaded or replicated by any means, without the written permission of the copyright owner (generally AlgaeBase). Fair usage of data in scientific publications is permitted.
original description
Saville-Kent W. 1880/82. A manual of the infusoria. London, Bogue 1: 460-461. [details]
original description Kent, W.S. (1880-1881). A manual of the infusoria, including a description of all known flagellate, ciliate, and tentaculiferous protozoa, British and foreign and an account of the organization and affinities of the sponges. Vol. I pp. 289-720. London., available online at https://archive.org/details/manualofinfusori18081kent [details] original description (of Dinophysis diegensis Kofoid, 1907) Kofoid, C.A. (1907). Dinoflagellata of the San Diego Region, III. Description of new species. <em>University of California publications. Zoology.</em> 3: 299-304. (look up in RoR) [details] context source (HKRMS) Hodgkiss, I. J.; Chan, B. S. S. (1987). Phytoplankton dynamics in Tolo Harbour. <em>In: Morton B, editor. Asian Marine Biology 4.Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong.</em> 103-112. [details] context source (Bermuda) Sterrer, W. (1986). Marine fauna and flora of Bermuda: a systematic guide to the identification of marine organisms. <em>Wiley-Interscience Publication. Wiley.</em> 742 pp (Nemertini part). [details] Available for editors basis of record Gómez, F. (2005). A list of free-living dinoflagellate species in the world's oceans. <em>Acta Bot. Croat.</em> 64(1): 129-212. [details] additional source Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2024). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details] additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details] additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details] additional source Martin, J. L.; LeGresley, M. M.; Strain P. M.; Clement, P. (1999). Phytoplankton monitoring in the southwest Bay of Fundy during 1993-96. <em>Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2265.</em> 4: 1-132. [details] additional source Abé, T.H. (1967). The armoured Dinoflagellata: II. Prorocentridae and Dinophysidae (B) - <i>Dinophysis</i> and its allied genera. <em>Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory.</em> 2: 37-78. [details] Available for editors additional source Fukuyo Y., Takano H., Chihara M. & Matsuoka K. 1990. <i>Red tide organisms in Japan – an illustrated taxonomic guide</i>. Uchida Rokakuho, Tokyo. 430 pp. [details] additional source Karunasagar I., Segar K. & Karunasagar I. 1989. Potentially toxic dinoflagellates in shellfish harvesting areas along the coast of Karnataka State (India). In : <i>Red tide: Biology, Environmental Science, and Toxicology</i> (Ed. by T. Okaichi, D.M. Anderson & T. Nemoto), pp. 65 - 68. Elsevier, New York. [details] additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details] additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in RoR) [details] Available for editors additional source Lakkis, S. (2011). Le phytoplancton marin du Liban (Méditerranée orientale): biologie, biodiversité, biogéographie. Aracne: Roma. ISBN 978-88-548-4243-4. 293 pp. (look up in RoR) [details] additional source Chang, F.H.; Charleston, W.A.G.; McKenna, P.B.; Clowes, C.D.; Wilson, G.J.; Broady, P.A. (2012). Phylum Myzozoa: dinoflagellates, perkinsids, ellobiopsids, sporozoans, in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2012). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 3. Kingdoms Bacteria, Protozoa, Chromista, Plantae, Fungi. pp. 175-216. [details] additional source Kofoid, C.A.; Skogsberg, T. (1928). Reports on the scientific results of the expedition to the Eastern Tropical Pacific, in charge of Alexander Agassiz, by the U.S. Fish Commission Steamer "Albatross" from October 1904 to March 1905, Lieut. Commander L.M. Garrett, U.S.N., Commanding. [No.] XXXV. The Dinoflagellata: the Dinophysoidae. <em>Memoirs of the Museum of Comparative Zoölogy, at Harvard College, Cambridge, Mass.</em> 51: 1-766., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/4365822 [details] Available for editors additional source Balech, E. (1951). Sobre dos variedades de Dinophysis caudata Kent. <em>Comunic. Zool. Mus. Hist. Nat. Montevideo.</em> 3(60): 1-9. [details] Available for editors additional source Balech, E. (2002). Dinoflagelados tecados tóxicos en el Cono Sur Americano. <em>In: Sar, E.A., Ferrario, M.E. & Reguera, B. (Eds.). Floraciones Algales Nocivas en el Cono Sur Americano. Instituto Español de Oceanografía.</em> pp. 123-144. [details] Available for editors additional source Campbell, P.H. (1973). Studies on brackish water phytoplankton. UNC.SG.73.07. pp. 1-406. Chapel Hill: Sea Grant Publications, University of North Carolina. [details] Available for editors ecology source Nishitani, G.; Nagai, S.; Takano, Y.; Sakiyama, S.; Baba, K.; Kamiyama, T. (2008). Growth characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of the marine dinoflagellate Dinophysis infundibulus (Dinophyceae). <em>Aquatic Microbial Ecology.</em> 52: 209-221., available online at https://doi.org/10.3354/ame01233 [details] ecology source Nishitani, G.; Nagai, S.; Sakiyama, S.; Kamiyama, T. (2008). Successful cultivation of the toxic dinoflagellate Dinophysis caudata (Dinophyceae). <em>Plankton and Benthos Research.</em> 3(2): 78-85., available online at https://doi.org/10.3800/pbr.3.78 [details] ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details]  Present Present  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
Published in AlgaeBase
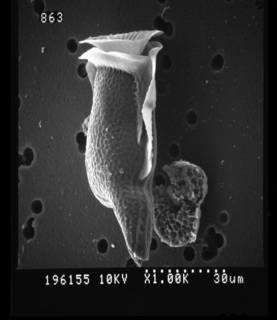
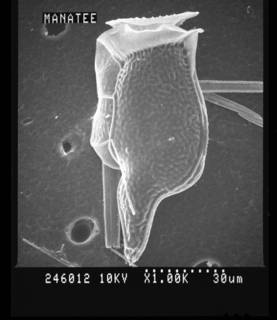
 Published in AlgaeBase  (from synonym Dinophysis diegensis Kofoid, 1907) (from synonym Dinophysis diegensis Kofoid, 1907)To Biodiversity Heritage Library (18 publications) To Biodiversity Heritage Library (9 publications) (from synonym Dinophysis diegensis Kofoid, 1907) To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL) To Dyntaxa To European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) To GenBank (117 nucleotides; 53 proteins) To NMNH Extant Collection (196155.jpg) To NMNH Extant Collection (246012.jpg) To PESI To PESI (from synonym Dinophysis diegensis Kofoid, 1907) To ITIS |