WoRMS taxon details
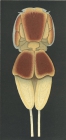
Echthrogaleus coleoptratus (Guérin-Méneville, 1837)
135976 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:135976)
accepted
Species
Dinematura braccata Dana, 1849-1852 · unaccepted (synonym)
Dinematura coleoptrata Guérin-Méneville, 1837 · unaccepted (synonym)
Dinemoura affinis Milne Edwards, 1840 · unaccepted (synonym according to Cressey, 1967)
Dinemoura alata Milne Edwards, 1836 · unaccepted (synonym)
Dinemoura braccata (Dana, 1852) · unaccepted (synonym)
Dinemoura coleoptrata (Guérin-Méneville, 1837) · unaccepted (synonym)
Echthrogaleus affinis (Milne Edwards, 1840) · unaccepted (synonym)
Echthrogaleus braccatus (Dana, 1853) · unaccepted (synonymy)
Echthrogaleus perspicax Olsson, 1869 · unaccepted (synonym)
Nogaus braccatus Heller, 1865 · unaccepted
Nogaus luetkeni Norman, 1869 · unaccepted (synonym)
Pandarus alatus Johnston, 1835 · unaccepted (listed as synonym by Brian, 1912)
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
Guérin-Méneville, F.E. (1829-1843). Iconographie du régne animal de G. Cuvier. [Representation d'apres nature de l'une des especes les plus remarquables et souvent non encore figurees, de chaque genre d'animaux.Iconography of the animal kingdom by G. Cuvier.]. <em>Planches des Animaux invertébrés. Zoophytes. 2. Crustacées. A. Londres publisher. (Publication began in 1829).</em> :1-48, [ Copepods pl. 35, This plate was published in 1837.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27813845 [details] 
(of Dinematura coleoptrata Guérin-Méneville, 1837) Guérin-Méneville, F.E. (1829-1843). Iconographie du régne animal de G. Cuvier. [Representation d'apres nature de l'une des especes les plus remarquables et souvent non encore figurees, de chaque genre d'animaux.Iconography of the animal kingdom by G. Cuvier.]. <em>Planches des Animaux invertébrés. Zoophytes. 2. Crustacées. A. Londres publisher. (Publication began in 1829).</em> :1-48, [ Copepods pl. 35, This plate was published in 1837.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27813845 [details]
(of Dinematura coleoptrata Guérin-Méneville, 1837) Guérin-Méneville, F.E. (1829-1843). Iconographie du régne animal de G. Cuvier. [Representation d'apres nature de l'une des especes les plus remarquables et souvent non encore figurees, de chaque genre d'animaux.Iconography of the animal kingdom by G. Cuvier.]. <em>Planches des Animaux invertébrés. Zoophytes. 2. Crustacées. A. Londres publisher. (Publication began in 1829).</em> :1-48, [ Copepods pl. 35, This plate was published in 1837.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27813845 [details]
Distribution cosmopolitan, recorded frthe Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, less common in the Indian Ocean
Distribution cosmopolitan, recorded frthe Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, less common in the Indian Ocean [details]
Walter, T.C.; Boxshall, G. (2025). World of Copepods Database. Echthrogaleus coleoptratus (Guérin-Méneville, 1837). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=135976 on 2025-07-06
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
Nomenclature
original description
Guérin-Méneville, F.E. (1829-1843). Iconographie du régne animal de G. Cuvier. [Representation d'apres nature de l'une des especes les plus remarquables et souvent non encore figurees, de chaque genre d'animaux.Iconography of the animal kingdom by G. Cuvier.]. <em>Planches des Animaux invertébrés. Zoophytes. 2. Crustacées. A. Londres publisher. (Publication began in 1829).</em> :1-48, [ Copepods pl. 35, This plate was published in 1837.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27813845 [details] 
original description (of Echthrogaleus perspicax Olsson, 1869) Olsson, P. (1869). Prodromus Faunae Copepodorum Parasitantium Scandinaviae. [Prodrome of the Copepod Parasitic Fauna of Scandinavia.]. <em>Acta Universitatis Lundensis (Acta Universitets Lunds).</em> 5(III)(8):1-49, pls. 1-2. [details]
original description (of Nogaus luetkeni Norman, 1869) Norman, A.M. (1869). Last report on dredging among the Shetland Isles. Part 2. On the Crustacea, Tunicata, Polyzoa, Echinodermata, Actinozoa, Hydrozoa, and Porifera. <em>In: Report of the thirty-eighth meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science; held in Norwich in August 1868. London 1869.</em> pp. 247–336, (Amphipoda, pp. 273–288) (Porifera, pp. 327-335)., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/29387922 [details]
original description (of Dinemoura alata Milne Edwards, 1836) Guérin-Méneville, F.E. (1829-1843). Iconographie du régne animal de G. Cuvier. [Representation d'apres nature de l'une des especes les plus remarquables et souvent non encore figurees, de chaque genre d'animaux.Iconography of the animal kingdom by G. Cuvier.]. <em>Planches des Animaux invertébrés. Zoophytes. 2. Crustacées. A. Londres publisher. (Publication began in 1829).</em> :1-48, [ Copepods pl. 35, This plate was published in 1837.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27813845 [details]
original description (of Dinemoura affinis Milne Edwards, 1840) Milne Edwards, H. (1840). Ordre des Copépodes. [Order Copepoda]. <em>Histoire naturelle des Crustaces, comprenant l'anatomie, la physiologie et la classification de ces animaux. [In: Natural history of Crustacea, including the anatomy, physiology and classification of these animals]].</em> 3: 411-529., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/16103940 [details]
original description (of Nogaus braccatus Heller, 1865) Heller, C. (1865). Crustaceen. [Crustacea]. <em>Reise der Österreichischen Fregatte Novara um die Erdre, in den Jahren 1857, 1858, 1859 unter den Befehlen des Commodore B. von Wüllerstorf-Urbair, Zoologischer Theil, Kaiserlich-Königliche Hof- und Staatsdruckerei, Wien, Band.</em> 2 (Abtheilung 3): 1–280, pls. 1–25., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/13188320 [details]
original description (of Pandarus alatus Johnston, 1835) Johnston, G. (1835). Illustrations in British Zoology. Magazine of Natural History 8:202-205, figs. 21-22. (iv-1835) [details]
original description (of Dinematura braccata Dana, 1849-1852) Dana, J.D. (1853-1855). Crustacea. Part II. <em>In: United States Exploring Expedition. During the years 1838, 1839, 1840, 1841, 1842. Under the command of Charles Wilkes. U. S. N., C. Sherman Printer, Philadelphia.</em> 14: 691-1618. [1855, folio atlas pls. 1-96.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/40412910 [details]
original description (of Dinematura coleoptrata Guérin-Méneville, 1837) Guérin-Méneville, F.E. (1829-1843). Iconographie du régne animal de G. Cuvier. [Representation d'apres nature de l'une des especes les plus remarquables et souvent non encore figurees, de chaque genre d'animaux.Iconography of the animal kingdom by G. Cuvier.]. <em>Planches des Animaux invertébrés. Zoophytes. 2. Crustacées. A. Londres publisher. (Publication began in 1829).</em> :1-48, [ Copepods pl. 35, This plate was published in 1837.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27813845 [details]
basis of record Boxshall, G. (2001). Copepoda (excl. Harpacticoida), <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 252-268 (look up in IMIS) [details]
original description (of Echthrogaleus perspicax Olsson, 1869) Olsson, P. (1869). Prodromus Faunae Copepodorum Parasitantium Scandinaviae. [Prodrome of the Copepod Parasitic Fauna of Scandinavia.]. <em>Acta Universitatis Lundensis (Acta Universitets Lunds).</em> 5(III)(8):1-49, pls. 1-2. [details]
original description (of Nogaus luetkeni Norman, 1869) Norman, A.M. (1869). Last report on dredging among the Shetland Isles. Part 2. On the Crustacea, Tunicata, Polyzoa, Echinodermata, Actinozoa, Hydrozoa, and Porifera. <em>In: Report of the thirty-eighth meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science; held in Norwich in August 1868. London 1869.</em> pp. 247–336, (Amphipoda, pp. 273–288) (Porifera, pp. 327-335)., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/29387922 [details]
original description (of Dinemoura alata Milne Edwards, 1836) Guérin-Méneville, F.E. (1829-1843). Iconographie du régne animal de G. Cuvier. [Representation d'apres nature de l'une des especes les plus remarquables et souvent non encore figurees, de chaque genre d'animaux.Iconography of the animal kingdom by G. Cuvier.]. <em>Planches des Animaux invertébrés. Zoophytes. 2. Crustacées. A. Londres publisher. (Publication began in 1829).</em> :1-48, [ Copepods pl. 35, This plate was published in 1837.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27813845 [details]
original description (of Dinemoura affinis Milne Edwards, 1840) Milne Edwards, H. (1840). Ordre des Copépodes. [Order Copepoda]. <em>Histoire naturelle des Crustaces, comprenant l'anatomie, la physiologie et la classification de ces animaux. [In: Natural history of Crustacea, including the anatomy, physiology and classification of these animals]].</em> 3: 411-529., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/16103940 [details]
original description (of Nogaus braccatus Heller, 1865) Heller, C. (1865). Crustaceen. [Crustacea]. <em>Reise der Österreichischen Fregatte Novara um die Erdre, in den Jahren 1857, 1858, 1859 unter den Befehlen des Commodore B. von Wüllerstorf-Urbair, Zoologischer Theil, Kaiserlich-Königliche Hof- und Staatsdruckerei, Wien, Band.</em> 2 (Abtheilung 3): 1–280, pls. 1–25., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/13188320 [details]
original description (of Pandarus alatus Johnston, 1835) Johnston, G. (1835). Illustrations in British Zoology. Magazine of Natural History 8:202-205, figs. 21-22. (iv-1835) [details]
original description (of Dinematura braccata Dana, 1849-1852) Dana, J.D. (1853-1855). Crustacea. Part II. <em>In: United States Exploring Expedition. During the years 1838, 1839, 1840, 1841, 1842. Under the command of Charles Wilkes. U. S. N., C. Sherman Printer, Philadelphia.</em> 14: 691-1618. [1855, folio atlas pls. 1-96.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/40412910 [details]
original description (of Dinematura coleoptrata Guérin-Méneville, 1837) Guérin-Méneville, F.E. (1829-1843). Iconographie du régne animal de G. Cuvier. [Representation d'apres nature de l'une des especes les plus remarquables et souvent non encore figurees, de chaque genre d'animaux.Iconography of the animal kingdom by G. Cuvier.]. <em>Planches des Animaux invertébrés. Zoophytes. 2. Crustacées. A. Londres publisher. (Publication began in 1829).</em> :1-48, [ Copepods pl. 35, This plate was published in 1837.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27813845 [details]
basis of record Boxshall, G. (2001). Copepoda (excl. Harpacticoida), <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 252-268 (look up in IMIS) [details]
Taxonomy
redescription
Ho, J.S., W.C. Liu & C.L. Lin. (2013). Two species of Echthrogaleus (Copepoda: Siphonostomatoida: Pandaridae) parasitic on five species of sharks off the east coast of Taiwan. <em>Journal of the Fisheries Society of Taiwan.</em> 39(4): 247-255 (for 2012). [details] Available for editors  [request]
[request]
redescription Kabata, Z. (1979). Parasitic Copepoda of British Fishes. <em>The Ray Society, London.</em> 152: i-xii, 1-468, figs. 1-203. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
redescription Shiino, S.M. (1954). Copepods parasitic on Japanese fishes. 5. Five species of the family Pandaridae. Report of the Faculty of Fisheries, Prefectural University of Mie 1(3):291-332, figs. 1-19. (30-vii-1954) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
redescription Kabata, Z. (1979). Parasitic Copepoda of British Fishes. <em>The Ray Society, London.</em> 152: i-xii, 1-468, figs. 1-203. [details] Available for editors
redescription Shiino, S.M. (1954). Copepods parasitic on Japanese fishes. 5. Five species of the family Pandaridae. Report of the Faculty of Fisheries, Prefectural University of Mie 1(3):291-332, figs. 1-19. (30-vii-1954) [details] Available for editors
Other
context source (Deepsea)
Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO. The Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS), available online at http://www.iobis.org/ [details]
additional source Barnard, K.H. (1955). South African parasitic Copepoda. <em>Annals of the South African Museum.</em> 41(5):223-312, figs. 1-33. (ii-1955). [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Hogans, W.E. (1995). Parasitic Copepoda in the collection of the Atlantic Reference Centre, St. Andrews, New Brunswick, Canada. <em>Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences.</em> Report no. 2028:1-6. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Guérin-Méneville, F.E. (1829-1843). Iconographie du régne animal de G. Cuvier. [Representation d'apres nature de l'une des especes les plus remarquables et souvent non encore figurees, de chaque genre d'animaux.Iconography of the animal kingdom by G. Cuvier.]. <em>Planches des Animaux invertébrés. Zoophytes. 2. Crustacées. A. Londres publisher. (Publication began in 1829).</em> :1-48, [ Copepods pl. 35, This plate was published in 1837.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27813845 [details]
additional source Heegaard, P.E. (1962). Parasitic Copepoda from Australian waters. Records of the Australian Museum 25(9):149-234, figs. 1-250. (28-v-1962) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Hewitt, G.C. (1967). Some New Zealand parasitic Copepoda of the family Pandaridae. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 1(2):180-264, figs. 1-159. (vi-1967) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Ho, J.S. & I.H. Kim. (1996). Copepods parasitic on fishes of western North Pacific. Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory 37(3/6):275-303. (xii-1996; errata sheet) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Kabata, Z. (1979). Parasitic Copepoda of British Fishes. <em>The Ray Society, London.</em> 152: i-xii, 1-468, figs. 1-203. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Kabata, Z. (1988). Schistobrachia pilgrimi sp. nov. (Copepoda: Lernaeopodidae), parasitic on the gills of Harriotta raleighana Goode & Bean, 1895 (Pisces: Holocephali). New Zealand Journal of Zoology 15(4):551-555. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Markevich, A.P. (1956). Paraziticheskie veslonogie ryb SSSR. [Parasitic copepods of fishes of the USSR.]. <em>Akademiya Nauk Ukraine SSR, Institut Zoology, Kiev.</em> 259 pp. figs. 1-153. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Montú, M.A. (1997). Records of parasitic copepods of sharks from the southwestern Atlantic. Nauplius, Rio Grande 4:179-180. (dated 1996; published vii-1997) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Pilgrim, R.L.C. (1985). Parasitic Copepoda from marine coastal fishes in the Kaikoura-Banks Peninsula Region, South Island, New Zealand. With a key for their identification. Mauri Ora 12:13-53, figs. 1-63. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Pillai, N.K. (1985). Copepod Parasites of Marine Fishes. <em>In: The Fauna of India. Zoological Society of India, Calcutta.</em> 900pp., figs. 1-279.
page(s): 188 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Steenstrup, J.J.S. & C.F. Lütken. (1861). Bidrag til kundskab om det aabne havs snyltekrebs og lernæer samt om nogle andre nye eller hidtil kun ufuldstændigt kjendte parasitiske Copepoder. [Contribution to knowledge about the open sea parasitic crabs and mud crabs and about some other new or hitherto only incompletely known parasitic Copepods.]. <em>Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskabs Skrifter, Naturhistorisk og Mathematisk Afdeling, Kjöbenhavn.</em> (5)5: 343-432, pls. 1-15., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/39308528 [details]
additional source Wilson, C.B. (1907). North American parasitic copepods belonging to the family Caligidae. Parts 3 and 4.- A revision of the Pandarinae and the Cecropinae. Proceedings of the United States National Museum 33(1573):323-490, pls. 17-43. (31-xii-1907). [details]
additional source Webber, W.R., G.D. Fenwick, J.M. Bradford-Grieve, S.G. Eagar, J.S. Buckeridge, G.C.B. Poore, E.W. Dawson, L. Watling, J.B. Jones, J.B.J. Wells, N.L. Bruce, S.T. Ahyong, K. Larsen, M.A. Chapman, J. Olesen, J.S. Ho, J.D. Green, R.J. Shiel, C.E.F. Rocha, A. Lörz, G.J. Bird & W.A. Charleston. (2010). Phylum Arthropoda Subphylum Crustacea: shrimps, crabs, lobsters, barnacles, slaters, and kin. <em>in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2010). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 2. Kingdom Animalia: Chaetognatha, Ecdysozoa, Ichnofossils.</em> pp. 98-232 (COPEPODS 21 pp.). [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source Carli, A. & C.L. Bruzzone. (1968). Studio su Echthrogaleus coleoptratus (Guérin 1840) parassita di Prionace glauca (Linneo) rinvenuto nel Mare Ligure. [Study on Echthrogaleus coleoptratus (Guérin 1840) parasite of Prionace glauca (Linnaeus) found in the Ligurian Sea.]. <em>Annali del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale 'Giacomo Doria', Genova.</em> 77:560-573, figs. 1-2, pls. 1-2, tab. 1. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Wilson, C.B. (1932). The copepods of the Woods Hole region, Massachusetts. <em>Bulletin of the United States National Museum.</em> 158:1-635, figs. 1-316, pls. 1-41. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Kumar, K.A. (1990). Studies on copepod parasites on elasmobranchs of Kerala Coast. <em>Ph.D. Thesis, The Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin, India.</em> 286 pp. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Barnard, K.H. (1955). South African parasitic Copepoda. <em>Annals of the South African Museum.</em> 41(5):223-312, figs. 1-33. (ii-1955). [details] Available for editors
additional source Hogans, W.E. (1995). Parasitic Copepoda in the collection of the Atlantic Reference Centre, St. Andrews, New Brunswick, Canada. <em>Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences.</em> Report no. 2028:1-6. [details] Available for editors
additional source Guérin-Méneville, F.E. (1829-1843). Iconographie du régne animal de G. Cuvier. [Representation d'apres nature de l'une des especes les plus remarquables et souvent non encore figurees, de chaque genre d'animaux.Iconography of the animal kingdom by G. Cuvier.]. <em>Planches des Animaux invertébrés. Zoophytes. 2. Crustacées. A. Londres publisher. (Publication began in 1829).</em> :1-48, [ Copepods pl. 35, This plate was published in 1837.]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/27813845 [details]
additional source Heegaard, P.E. (1962). Parasitic Copepoda from Australian waters. Records of the Australian Museum 25(9):149-234, figs. 1-250. (28-v-1962) [details] Available for editors
additional source Hewitt, G.C. (1967). Some New Zealand parasitic Copepoda of the family Pandaridae. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 1(2):180-264, figs. 1-159. (vi-1967) [details] Available for editors
additional source Ho, J.S. & I.H. Kim. (1996). Copepods parasitic on fishes of western North Pacific. Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory 37(3/6):275-303. (xii-1996; errata sheet) [details] Available for editors
additional source Kabata, Z. (1979). Parasitic Copepoda of British Fishes. <em>The Ray Society, London.</em> 152: i-xii, 1-468, figs. 1-203. [details] Available for editors
additional source Kabata, Z. (1988). Schistobrachia pilgrimi sp. nov. (Copepoda: Lernaeopodidae), parasitic on the gills of Harriotta raleighana Goode & Bean, 1895 (Pisces: Holocephali). New Zealand Journal of Zoology 15(4):551-555. [details] Available for editors
additional source Markevich, A.P. (1956). Paraziticheskie veslonogie ryb SSSR. [Parasitic copepods of fishes of the USSR.]. <em>Akademiya Nauk Ukraine SSR, Institut Zoology, Kiev.</em> 259 pp. figs. 1-153. [details] Available for editors
additional source Montú, M.A. (1997). Records of parasitic copepods of sharks from the southwestern Atlantic. Nauplius, Rio Grande 4:179-180. (dated 1996; published vii-1997) [details] Available for editors
additional source Pilgrim, R.L.C. (1985). Parasitic Copepoda from marine coastal fishes in the Kaikoura-Banks Peninsula Region, South Island, New Zealand. With a key for their identification. Mauri Ora 12:13-53, figs. 1-63. [details] Available for editors
additional source Pillai, N.K. (1985). Copepod Parasites of Marine Fishes. <em>In: The Fauna of India. Zoological Society of India, Calcutta.</em> 900pp., figs. 1-279.
page(s): 188 [details] Available for editors
additional source Steenstrup, J.J.S. & C.F. Lütken. (1861). Bidrag til kundskab om det aabne havs snyltekrebs og lernæer samt om nogle andre nye eller hidtil kun ufuldstændigt kjendte parasitiske Copepoder. [Contribution to knowledge about the open sea parasitic crabs and mud crabs and about some other new or hitherto only incompletely known parasitic Copepods.]. <em>Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskabs Skrifter, Naturhistorisk og Mathematisk Afdeling, Kjöbenhavn.</em> (5)5: 343-432, pls. 1-15., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/39308528 [details]
additional source Wilson, C.B. (1907). North American parasitic copepods belonging to the family Caligidae. Parts 3 and 4.- A revision of the Pandarinae and the Cecropinae. Proceedings of the United States National Museum 33(1573):323-490, pls. 17-43. (31-xii-1907). [details]
additional source Webber, W.R., G.D. Fenwick, J.M. Bradford-Grieve, S.G. Eagar, J.S. Buckeridge, G.C.B. Poore, E.W. Dawson, L. Watling, J.B. Jones, J.B.J. Wells, N.L. Bruce, S.T. Ahyong, K. Larsen, M.A. Chapman, J. Olesen, J.S. Ho, J.D. Green, R.J. Shiel, C.E.F. Rocha, A. Lörz, G.J. Bird & W.A. Charleston. (2010). Phylum Arthropoda Subphylum Crustacea: shrimps, crabs, lobsters, barnacles, slaters, and kin. <em>in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2010). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 2. Kingdom Animalia: Chaetognatha, Ecdysozoa, Ichnofossils.</em> pp. 98-232 (COPEPODS 21 pp.). [details] Available for editors
additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source Carli, A. & C.L. Bruzzone. (1968). Studio su Echthrogaleus coleoptratus (Guérin 1840) parassita di Prionace glauca (Linneo) rinvenuto nel Mare Ligure. [Study on Echthrogaleus coleoptratus (Guérin 1840) parasite of Prionace glauca (Linnaeus) found in the Ligurian Sea.]. <em>Annali del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale 'Giacomo Doria', Genova.</em> 77:560-573, figs. 1-2, pls. 1-2, tab. 1. [details] Available for editors
additional source Wilson, C.B. (1932). The copepods of the Woods Hole region, Massachusetts. <em>Bulletin of the United States National Museum.</em> 158:1-635, figs. 1-316, pls. 1-41. [details] Available for editors
additional source Kumar, K.A. (1990). Studies on copepod parasites on elasmobranchs of Kerala Coast. <em>Ph.D. Thesis, The Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin, India.</em> 286 pp. [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
Distribution cosmopolitan, recorded frthe Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, less common in the Indian Ocean [details]Unreviewed
Habitat parasitic species (host: e.g. Prionace glauca, Blue shark) [details]
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (10 publications) (from synonym Dinematura braccata Dana, 1849-1852)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (38 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Echthrogaleus braccatus (Dana, 1853))
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Echthrogaleus coleoptratus)
To GenBank (8 nucleotides; 2 proteins)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (1 record) (from synonym Echthrogaleus braccatus (Dana, 1853))
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (78 records)
To ITIS
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (38 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Echthrogaleus braccatus (Dana, 1853))
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Echthrogaleus coleoptratus)
To GenBank (8 nucleotides; 2 proteins)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (1 record) (from synonym Echthrogaleus braccatus (Dana, 1853))
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (78 records)
To ITIS