| About | | Search taxa | | Taxon tree | | Checklist | | Attributes | | Photogallery | | Stats | | Log in |
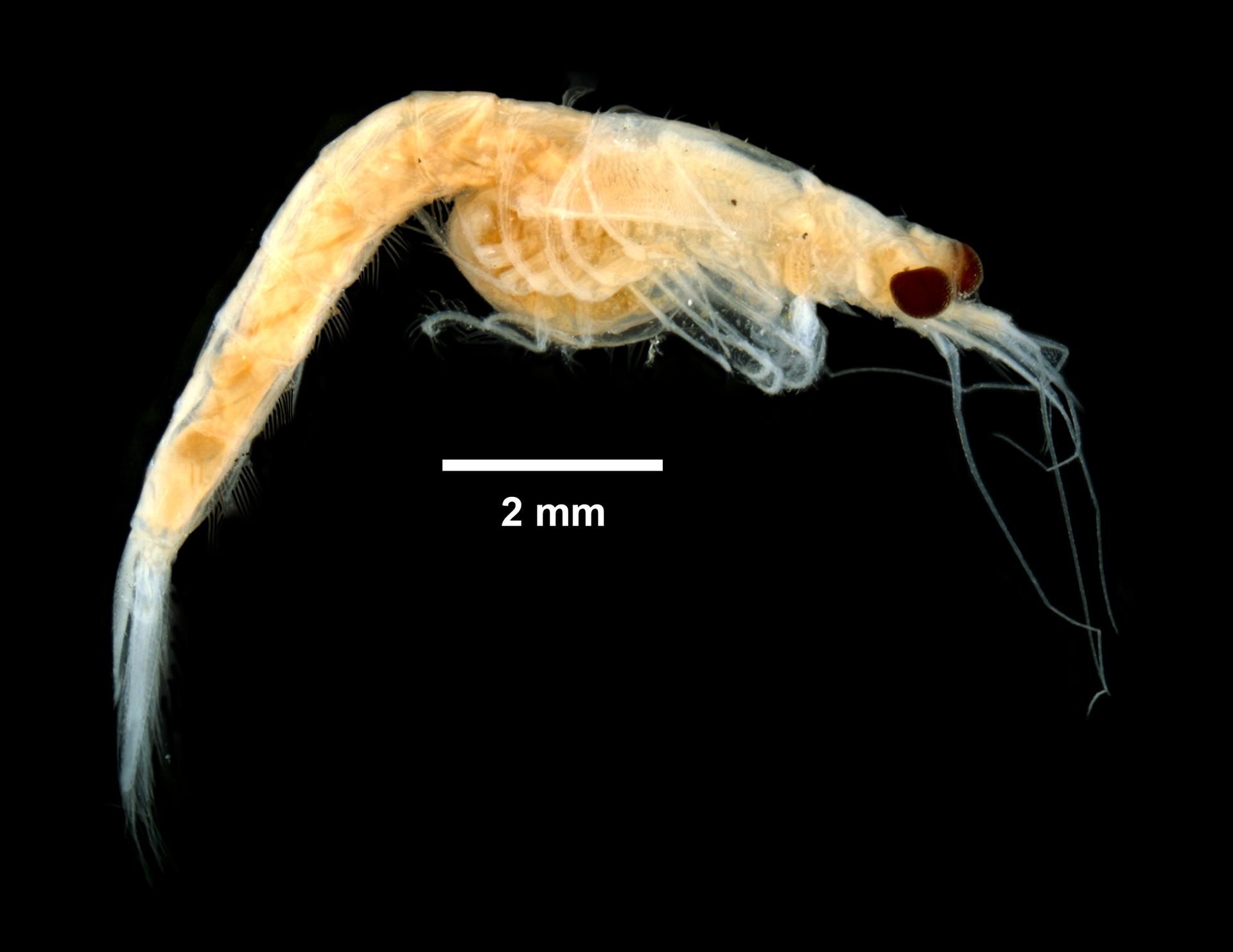
WoRMS taxon detailsNeomysis americana (S.I. Smith, 1873)
157807 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:157807)
accepted
Species
Mysis americana S. I. Smith, 1873 · unaccepted (basionym)
marine,
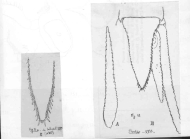
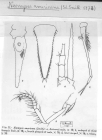
(of Mysis americana S. I. Smith, 1873) Smith, S. I. (1873). Report upon the invertebrate animals of Vineyard Sound and the adjacent waters, with an account of the physical characters of the region. <em>Rep. Comm. Fish Fish., 1871 and 1872.</em> pp. 295-747.
page(s): 552-553 [details]
Depth range 0-240m
Depth range 0-240m [details] Distribution Gulf of St. Lawrence (unspecified region), Saguenay Fjord, upstream and downstream part of middle St. Lawrence estuary,...
Distribution Gulf of St. Lawrence (unspecified region), Saguenay Fjord, upstream and downstream part of middle St. Lawrence estuary, southern Gaspe waters (Baie des Chaleurs, Gaspe Bay to American, Orphan and Bradelle banks; eastern boundary: eastern Bradelle Valley), Magdalen Islands (from eastern Bradelle valley to the west, as far as Cape North, including the Cape Breton Channel), lower St. Lawrence estuary, middle North Shore (from Sept- Iles to Cape Whittle, including the Mingan Island), Prince Edward Island (from the northern tip of Miscou Island, N.B. to Cape Breton Island south of Cheticamp, including the Northumberland Strait and Georges Bay to the Canso Strait causeway), western slope of Newfoundland, including the southern part of the Strait of Belle Isle but excluding the upper 50m in the area southwest of Newfoundland; southwestern slope of NL. [details]
Mees, J.; Meland, K.; Väinölä, R. (Eds) (2012 onwards). World List of Lophogastrida, Stygiomysida and Mysida. Neomysis americana (S.I. Smith, 1873). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=157807 on 2025-07-06
Date action by
Nomenclatureoriginal description
(of Mysis americana S. I. Smith, 1873) Smith, S. I. (1873). Report upon the invertebrate animals of Vineyard Sound and the adjacent waters, with an account of the physical characters of the region. <em>Rep. Comm. Fish Fish., 1871 and 1872.</em> pp. 295-747. page(s): 552-553 [details] Othercontext source (Schelde)
Van Ryckegem, G.; Van Braeckel, A.; Elsen, R.; Speybroeck, J.; Vandevoorde, B.; Mertens, W.; Breine, J.; De Beukelaer, J.; De Regge, N.; Hessel, K.; Soors, J.; Terrie, T.; Van Lierop, F.; Van den Bergh, E. (2016). MONEOS – Geïntegreerd datarapport INBO: Toestand Zeeschelde 2015: monitoringsoverzicht en 1ste lijnsrapportage Geomorfologie, diversiteit Habitats en diversiteit Soorten. <em>Rapport van het Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek, INBO.R.2016.12078839. Instituut voor Natuur- en Bosonderzoek: Brussel.</em> 178 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details] additional source Hanamura, Y.; Kase, T. (2002). Marine cave mysids of the genus Palaumysis (Crustacea: Mysidacea), with a description of a new species from the Philippines. <em>Journal of Natural History.</em> 36: 253-263. (look up in IMIS), available online at https://doi.org/10.1080/00222930010004241 [details] Available for editors additional source Müller, H. G. (1993). World catalogue and bibliography of the recent Mysidacea. 238p. [details] Available for editors additional source Kathman, R.D., W.C. Austin, J.C. Saltman & J.D. Fulton (1986): Identification manual of the Mysidacea and Euphausiacea of the northeast Pacific. - Can. Spec. Publ. Fish. Aquat.Sci., 93: 1-411 [details] Available for editors additional source Tattersall, W.M.; Tattersall, O.S. (1951). The British Mysidacea. <em>Ray Society, London.</em> 1-460, figs. 1-118. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors additional source Fockedey, N.; Mees, J. (1999). Feeding of the hyperbenthic mysid Neomysis integer in the maximum turbidity zone of the Elbe, Westerschelde and Gironde estuaries. <em>Journal of Marine Systems.</em> 22, 207-228. [details] Available for editors additional source Escobar-Briones, E.; Soto, L. A. (1991). Biogeografia de los Misidáceos (Crustacea: Peracarida) del Golfo de México. <em>Caribb. J. Sci.</em> 27 (1-2): 80-89. [details] Available for editors additional source Tattersall, W. M. (1951). A review of the Mysidacea of the United States National Museum. <em>Smithsonian Institution United States National Museum Bulletin.</em> 201: 1-292., available online at https://play.google.com/store/books/details?id=-vhMAAAAYAAJ&rdid=book--vhMAAAAYAAJ [details] Available for editors additional source Raymont, J.E.G. & R.J. Conover. (1961). Further investigations on the carbohydrate content of marine zooplankton. Limnology and Oceanography 6(2):154-164, tabs. 1-6. (iv-1964) [details] Available for editors additional source Tattersall, O.S. (1954). Shallow-water Mysidacea from the St. Lawrence estuary, Eastern Canada. The Canadian Field-naturalist 68(4): 143-154 [details] Available for editors additional source Beeton, A. M.; Bowers, J. A. (1982). Vertical migration of Mysis relicta Loven. <em>Hydrobiologia.</em> 93 (1-2): 53-61. [details] additional source Grabe, S.A. (1981). Occurence of Mysidopsis almyra BOWMAN, 1964 (Mysidacea) in the Patapsco River Estuary (upper Chesapeake Bay), Maryland, U.S.A. <em>Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash.</em> 94 (3): 863-865. [details] additional source Herman, S.S. 1962. Spectral sensitivity and phototaxis in the opossum shrimp, Neomysis americana Smith.-- The Biological Bulletin 123 (3): 562-570. [details] Available for editors additional source Price, W.W.; Vodopich, D.S. (1979). Occurence of Mysidopsis almyra (Mysidacea, Mysidae) on the east coast of Florida, U.S.A. <em>Crustaceana.</em> 36 (2): 194-196. [details] Available for editors additional source Verslycke, T.; Fockedey, N.; McKenney, C. L.; Roast, S. D.; Jones, M. B.; Mees, J.; Janssen, C. R. (2004). Mysids as potential test organisms for the evaluation of environmental endocrine disruption: a review. <em>Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry.</em> 23(5), 1219-1234. [details] additional source Wigley, R. L.; Burns, B. R. (1971). Distribution and biology of mysids (Crustacea, Mysidacea) from the Atlantic coast of the U.S. in the NMFS Woods Hole collection. <em>Fish. Bull.</em> 69 (4): 717-746. [details] Available for editors additional source Williams, A.B. 1972. A ten-year study of meroplankton in North Carolina estuaries: mysid shrimps.-- Chesapeake Science 13 (4): 254-262. [details] Available for editors additional source Williams, A.B., T.E. Bowman, & D.M. Damkaer. 1974. Distribution, variation, and supplemental description of the opossum shrimp, Neomysis americana (Crustacea: Mysidacea).-- Fishery Bulletin 72: 835-842. [details] Available for editors additional source Bergström, U.; Englund, G. (2004). Spatial scale, heterogeneity and functional responses. <em>Journal of Animal Ecology.</em> 73 : 487-493. [details] Available for editors additional source Clutter, R.I. (1969). Microdistribution and social behavior of pelagic mysids. <em>J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.</em> 3:125-155. [details] Available for editors additional source Almeida Prado-Por, M.S. de. (1973). Distribution of Mysidacea (Crustacea) in the Cananeia region. -. <em>Bolm. Fac. Fil. S. Paulo (Zool. & Biol. mar.), N.S. 30: 395-417.</em> [details] Available for editors additional source D.L. TAYLOR (2004). Immunological detection of winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus) eggs and juveniles in the stomach contents of crustacean predators J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 301 : 55-73 [details] Available for editors additional source GREENE, K. (2002). Beach Nourishment: A Review of the Biological and Physical Impacts. ASMFC Habitat Management Series # 7. Washington DC. 69 pp. : [details] Available for editors additional source HERMAN, S.S. (1963). Studies on the life history and vertical migration of the opossum shrimp, Neomysis americana Smith. - Diss. Abstr., 23: 2634. [development [details] Available for editors additional source HERMAN, S.S. (1963). Vertical migration of the opossum shrimp, Neomysis americana Smith. - Limnol. Oceanogr., 8: 228-238 [details] Available for editors additional source JUANES F, BUCKEL JA, SCHARF FS (2001). Predatory behaviour and selectivity of a primary piscivore: comparison of fish and non-fish prey MEPS 217:157-165 : [details] Available for editors additional source MAUCHLINE, J. (1971). Seasonal occurence of mysids (Crustacea) and evidence of social behaviour. - J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K., 51: 809-825. [biology, ecology [details] Available for editors additional source MAUCHLINE, J. (1971). The biology of Neomysis integer (Crustacea, Mysidacea). - J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K., 51: 347-354 [details] Available for editors additional source Mees, J.; Hamerlynck, O. (1992). Spatial community structure of the winter hyperbenthos of the Schelde estuary, the netherlands and the adjacent coastal waters. <em>Netherlands Journal of Sea Research.</em> 29(4): 357-370. [details] Available for editors additional source ROAST, S.D.; WIDDOWS, J.; JONES, M.B. (2000). Egestion rates of the estuarine mysid Neomysis integer (Peracarida : Mysidacea) in relation to a variable environment J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 245 : 69-81 [details] Available for editors additional source SORBE, J.C. (1991). Biologia del Misidàceo suprabentónico Schistomysis ornata (Sars, 1864) en la plataforma continental aquitana. - Actas V Simp. Ibér. Estud. Bentos Mar., 1: 273-298. [biology [details] Available for editors additional source VAN DOLAH, R.F.; WENDT, P.H.; MARTORE, R.M.; LEVISEN, M.V. & ROUMILLAT, W.A. (1992). Final report for A physical and biological monitoring study of the Hilton Head beach nourishment project. Marine Resource Research Institute : [details] Available for editors additional source Verslycke, T.; Roast, S. D.; Widdows, J.; Jones, M. B.; Janssen, C. R. (2004). Cellular energy allocation and scope for growth in the estuarine mysid Neomysis integer (Crustacea: Mysidacea) following chlorpyrifos exposure: a method comparison. <em>Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology.</em> 306(1): 1-16., available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2003.12.022 [details] Available for editors additional source WILBER, D.H.; CLARKE, D.G.; RAY, G.L. & BURLAS, M. (2003). Response of surf zone fish to beach nourishment operations on the northern coast of New Jersey, USA. MEPS 250: 231-246 : [details] Available for editors additional source Winkler, G.; Dodson, J.; Bertrand, N.; Thivierge, D.; Vincent, W. (2003). Trophic coupling across the St. Lawrence River estuarine transition zone. <em>Marine Ecology Progress Series.</em> 251: 59-73., available online at https://doi.org/10.3354/meps251059 [details] Available for editors additional source WINKLER G, GREVE W (2002). Laboratory studies of the effect of temperature on growth, moulting and reproduction in the co-occurring mysids Neomysis integer and Praunus flexuosus MEPS 235:177-188 : [details] Available for editors  Present Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate Inaccurate  Introduced: alien Introduced: alien  Containing type locality Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
Alien species Two specimens sampled with Van Veen grab in 2010 in very shallow marine coastal waters in The Netherlands along the North Sea coast of Schiermonnikoog. [details]Depth range 0-240m [details] Habitat on sandy bottom, more often on coarse than on fine sand [details] From regional or thematic species database
Introduced species vector dispersal Argentinean part of the South Atlantic Ocean (Marine Region) Ships: general (ship boring) [details]Unreviewed
Distribution Gulf of St. Lawrence (unspecified region), Saguenay Fjord, upstream and downstream part of middle St. Lawrence estuary, southern Gaspe waters (Baie des Chaleurs, Gaspe Bay to American, Orphan and Bradelle banks; eastern boundary: eastern Bradelle Valley), Magdalen Islands (from eastern Bradelle valley to the west, as far as Cape North, including the Cape Breton Channel), lower St. Lawrence estuary, middle North Shore (from Sept- Iles to Cape Whittle, including the Mingan Island), Prince Edward Island (from the northern tip of Miscou Island, N.B. to Cape Breton Island south of Cheticamp, including the Northumberland Strait and Georges Bay to the Canso Strait causeway), western slope of Newfoundland, including the southern part of the Strait of Belle Isle but excluding the upper 50m in the area southwest of Newfoundland; southwestern slope of NL. [details]Habitat intertidal and infralittoral of the Gulf and estuary [details]
To Barcode of Life (441 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (31 publications) (from synonym Mysis americana S. I. Smith, 1873) To Biodiversity Heritage Library (41 publications) To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Neomysis americana) To GenBank (25 nucleotides; 21 proteins) (from synonym Mysis americana S. I. Smith, 1873) To GenBank (25 nucleotides; 21 proteins) To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (96 records) To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 083136) To ITIS |