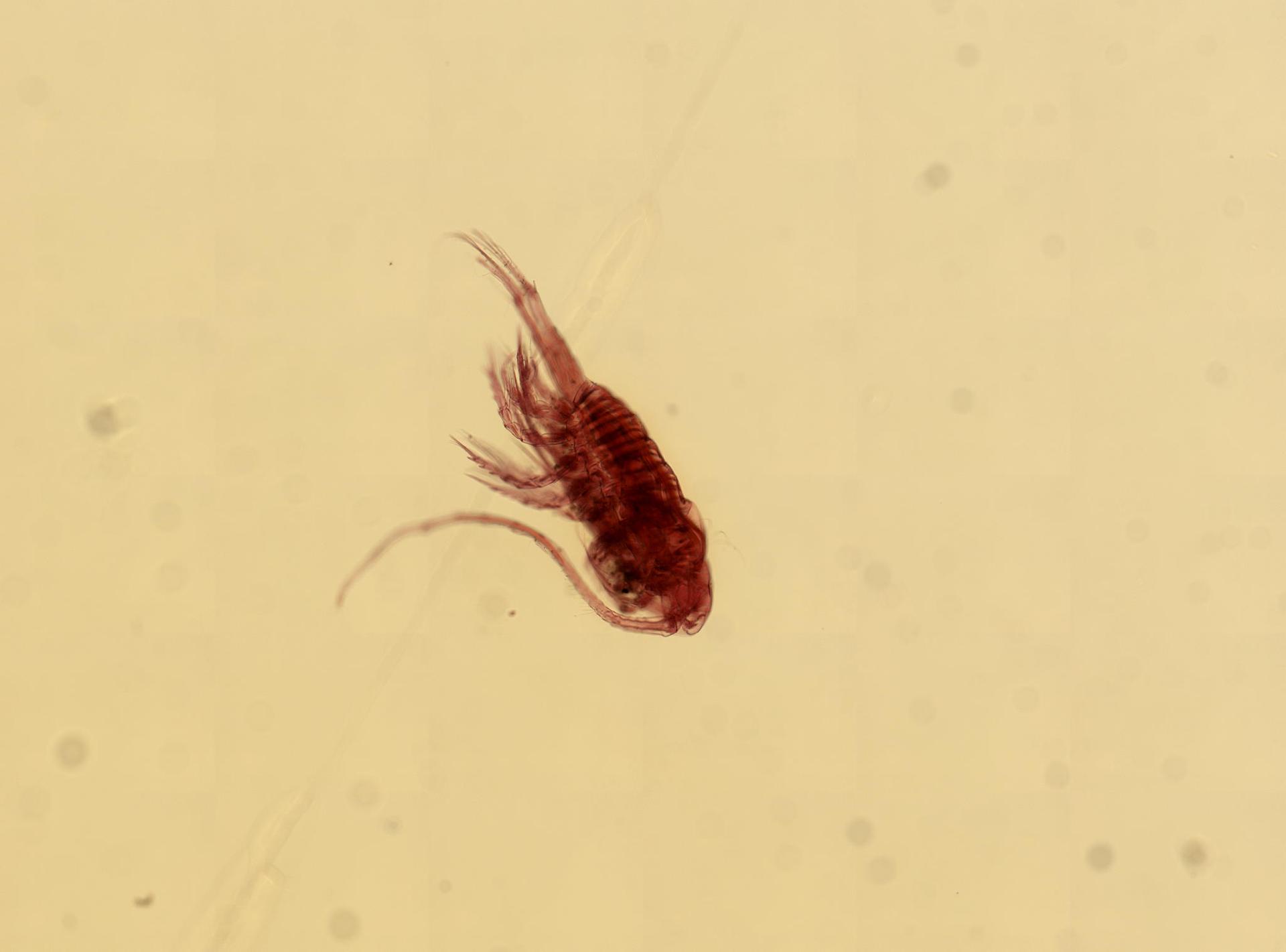
MSBIAS taxon details
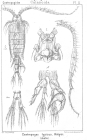
Centropages typicus Krøyer, 1849
104499 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:104499)
accepted
Species
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
Krøyer, H. (1849). Karcinologiske Bidrag (Fortsaettelse). [Carcinological Contributions (Continued)]. <em>Naturhistorisk Tidsskrift Ser. II.</em> 2(6): 561-609, pl. 6. (look up in IMIS)
page(s): 603 [details]
page(s): 603 [details]
Walter, T.C.; Boxshall, G. (2025). World of Copepods Database. Centropages typicus Krøyer, 1849. Accessed through: The UK Marine Environmental Data and Information Network (2025) Marine Species of the British Isles and Adjacent Seas (MSBIAS): a checklist of species derived from the UNICORN and Marine Recorder applications at: https://www.marinespecies.org/msbias/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=104499 on 2025-07-09
The UK Marine Environmental Data and Information Network (2025). Marine Species of the British Isles and Adjacent Seas (MSBIAS): a checklist of species derived from the UNICORN and Marine Recorder applications. Centropages typicus Krøyer, 1849. Accessed at: https://marinespecies.org/msbias/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=104499 on 2025-07-09
Date
action
by
original description
Krøyer, H. (1849). Karcinologiske Bidrag (Fortsaettelse). [Carcinological Contributions (Continued)]. <em>Naturhistorisk Tidsskrift Ser. II.</em> 2(6): 561-609, pl. 6. (look up in IMIS)
page(s): 603 [details]
context source (Deepsea) Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO. The Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS), available online at http://www.iobis.org/ [details]
context source (BeRMS 2020) Bio-environmental research group; Institute of Agricultural and Fisheries research (ILVO), Belgium; (2015): Zooplankton monitoring in the Belgian Part of the North Sea between 2009 and 2010. [details]
basis of record Boxshall, G. (2001). Copepoda (excl. Harpacticoida), <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 252-268 (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Brunel, P., L. Bosse & G. Lamarche. (1998). Catalogue of the marine invertebrates of the estuary and Gulf of St. Lawrence. <em>Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 126.</em> 405 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Roff, J.C. (1978). A guide to the marine flora and fauna of the Bay of Fundy: Copepoda: Calanoida. Fisheries and Marine Service Technical Report 823. 27 p. [details] Available for editors
additional source Muller, Y. (2004). Faune et flore du littoral du Nord, du Pas-de-Calais et de la Belgique: inventaire. [Coastal fauna and flora of the Nord, Pas-de-Calais and Belgium: inventory]. <em>Commission Régionale de Biologie Région Nord Pas-de-Calais: France.</em> 307 pp., available online at http://www.vliz.be/imisdocs/publications/145561.pdf [details]
additional source Arnaud, J., M. Brunet & J. Mazza. (1978). Studies on the midgut of Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida). <em>Cell and Tissue Research.</em> 187(2): 333-353, figs. 1-23, tabs. 1-2. [details] Available for editors
additional source Arnaud, J., M. Brunet & J. Mazza. (1987). Rôle des cellules B de l'intestin moyen chez Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida). [Role of midgut B cells in Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida).]. <em>Réproduction, Nutrition, et Développement.</em> 27(4): 817-827. [details] Available for editors
additional source Arnaud, J., M. Brunet & J. Mazza. (1988). Labral glands in Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida). I. Sites of synthesis. <em>Journal of Morphology.</em> 197(1): 21-32. [details] Available for editors
additional source Blades, P.I. (1977). Mating behavior of Centropages typicus (Copepoda: Calanoida). Marine Biology, Berlin 40(1):57-64, figs. 1-7. (25-ii-1977) [details] Available for editors
additional source Caparroy, P., M.T. Perez & F. Carlotti. (1998). Feeding behaviour of Centropages typicus in calm and turbulent conditions. Marine Ecology Progress Series 168:109-118. (9.vii.1998) [details] Available for editors
additional source Carlton, J.T. & J.B. Geller. (1993). Ecological roulette: the global transport of nonindigenous marine organisms. Science, New York 261:78-82. [details] Available for editors
additional source Cowles, T.J. & J.R. Strickler. (1983). Characterization of feeding activity patterns in the planktonic copepod Centropages typicus Kroyer under various food conditions. Limnology and Oceanography 28(1):106-115, figs. 1-11, tabs. 1-2. (i-1983) [details] Available for editors
additional source Dagg, M.J. (1978). Estimated, in situ, rates of egg production for the copepod Centropages typicus (Kroyer) in the New York bight. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 34(3):183-196, figs. 1-9, tab. 1. [details] Available for editors
additional source Dagg, M.J. & D.W. Grill. (1980). Natural feeding rates of Centropages typicus females in the New York Bight. Limnology and Oceanography 25(4):597-609, figs. 1-6, tabs. 1-2. (vii-1980) [details] Available for editors
additional source Grandori, R. (1925). Sulle sviluppo larvale di Centropages typicus Kroyer. [On the larval development of Centropages typicus Kroyer.]. <em>Rivista di Biologia.</em> 7:137-145, figs. 1-10. [details] Available for editors
additional source Gaudy, R. (1971). Étude expérimentale de la ponte chez trois espèces de Copépodes pélagiques (Centropages typicus, Acartia clausi et Temora stylifera). [Experimental study of spawning in three species of pelagic copepods (Centropages typicus, Acartia clausi and Temora stylifera).]. <em>Marine Biology, Berlin.</em> 9(1): 65-70, fig. 1, tab. 1. [details] Available for editors
additional source Gaudy, R. (1971). L'allongement antennulaire chez <i>Centropages typicus</i>, signification adaptative et utilité biométrique. [Antennular elongation in <i>Centropages typicus</i>, adaptive significance and biometric utility. <em>Rapports et Procès-Verbaux des Réunions de la Commission Internationale pour l'Exploration Scientifique de la Mer Mediterranée, Monaco.</em> 20(3): 363-365, fig. 1. [details] Available for editors
additional source Ianora, A. (1990). The effect of reproductive condition on egg production rates in the planktonic copepod Centropages typicus. Journal of Plankton Research 12(4):885-890. [details] Available for editors
additional source Grant, G.C. (1988). Seasonal occurrence and dominance of Centropages congeners in the Middle Atlantic Bight, USA. <em>In: Boxshall, G.A. & H.K. Schminke (eds.). Biology of Copepods. Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Copepoda. Developments in Hydrobiolology 47, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Hydrobiologia.</em> 47(167/168):227-237, figs. 1-3, tabs. 1-5. [details] Available for editors
additional source Guerrero, F., S. Nival & P. Nival. (1997). Egg production and viability in Centropages typicus: A laboratory study on the effect of food concentration. <em>Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom.</em> 77(1):257-260. [details] Available for editors
additional source Johnson, W.H. & J.E.G. Raymond. (1939). The reactions of the planktonic copepod, Centropages typicus, to light and gravity. Biological Bulletin, Woods Hole 77(2):200-215, tabs. 1-5. (x-1939) [details] Available for editors
additional source Ianora, A. & I. Buttino. (1990). Seasonal cycles in population abundances and egg production rates in the planktonic copepods Centropages typicus and Acartia clausi. Journal of Plankton Research 12(3):473-481. [details] Available for editors
additional source Ianora, A., A. Miralto & S. Vanucci. (1992). The surface attachment structure: a unique type of integumental formation in neustonic copepods. <em>Marine Biology, Berlin.</em> 113(3):401-407, figs. 1-5. [details] Available for editors
additional source Lawson, T.J. & G.D. Grice. (1970). The developmental stages of Centropages typicus Kroyer (Copepoda, Calanoida). Crustaceana, Leiden 18(2):187-208, figs. 1-137. (25-iii-1970) [details] Available for editors
additional source Lee, C.M. (1972). Structure and function of the spermatophore and its coupling device in the Centropagidae (Copepoda: Calanoida). Bulletin of Marine Ecology 8(1):1-20, figs. 1-10, pls. 1-10, tabs. 1-2. (ix-1972) [details] Available for editors
additional source Linko, A.K. (1907). Untersuchungen über das Plankton des Barents Meeres. [Investigations on the plankton of the Barents Sea.]. <em>Wissenschaftlich praktische Murman Expedition, St. Petersburg.</em> :1-247, figs.1-21. [details]
additional source McAden, D.C., G.N. Greene & W.B. Baker, Jr. (1987). First record of Centropages typicus Kroyer (Copepoda: Centropagidae) in the Gulf of Mexico. Texas Journal of Science 39(3):290-291. [details] Available for editors
additional source Muxagata, E.M. & J.A. Williams. (2004). The Mesozooplankton of the Solent-Southampton Water system: a photographic guide. Southampton Oceanography Centre, Southampton, U.K. 103 pp. [details] Available for editors
additional source Nival, S., M. Pagano & P. Nival. (1990). Laboratory study of the spawning rate of the calanoid copepods Centropages typicus: effect of fluctuating food concentration. Journal of Plankton Research 12(3):535-547. [details] Available for editors
additional source Pesta, O. (1928). Krebstiere oder Crustacea. I: Ruderfüsser oder Copepoda (1. Calanoida, 2. Cyclopoida) (3. Ordnung) [Crustaceans or Crustacea. I: Copepods (1. Calanoida, 2. Cyclopoida) (3rd order).]. <em>In: Dahl, F. (ed.). Die Tierwelt Deutschlands und der Angrenzenden Meeresteile nach Ihren Merkmalen und nach Ihrer Lebensweise. Fischer, Jena.</em> 9:1-136, figs. 1-115. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sars, G.O. (1902). Copepoda Calanoida, Parts VII & VIII, Centropagidae, Diaptomidae. <em>An Account of the Crustacea of Norway, with short descriptions and figures of all the species. Bergen Museum.</em> 4:73-96, pls. 49-64. [details]
additional source Razouls, C. (1973). Variations annuelles quantitatives de deux espèces dominantes de Copépodes planctoniques Centropages typicus et Temora stylifera de la région de Banyuls: Cycles biologiques et estimations de la production. I. Méthodologie et mise en évidence de l'importance quantitative de ces deux espèces par rapport à l'ensemble des Copépodes. [Annual quantitative variations of two dominant species of planktonic copepods Centropages typicus and Temora stylifera from the Banyuls region: Biological cycles and production estimates. I. Methodology and highlighting of the quantitative importance of these two species in relation to all copepods.]. <em>Cahiers de Biologie Marine.</em> 14(3):361-390, tabs. 1-11, annexe 1 & 2. [details] Available for editors
additional source Razouls, C. (1974). Variations annuelles quantitatives de deux espèces dominantes de Copépodes planctoniques Centropages typicus et Temora stylifera de la région de Banyuls: cycles biologiques et estimations de la production. III. Dynamique des populations et calcul de leur production. [Annual quantitative variations of two dominant species of planktonic copepods Centropages typicus and Temora stylifera from the Banyuls region: biological cycles and production estimates. III. Population dynamics and calculation of their production.]. <em>Cahiers de Biologie Marine.</em> 15(1):51-88, figs. 1-9, tabs. 1-4, annexe I & II. (15-ii-1974). [details] Available for editors
additional source Razouls, C. & C. Guinness. (1973). Variations annuelles quantitatives de deux espèces dominantes de Copépodes planctoniques Centropages typicus et Temora stylifera de la région de Banyuls: cycles biologiques et estimation de la production. II. Variations dimensionales et mesures de la croissance. [Annual quantitative variations of two dominant species of planktonic copepods Centropages typicus and Temora stylifera from the Banyuls region: biological cycles and production estimation. II. Dimensional variations and growth measurements.]. <em>Cahiers de Biologie Marine.</em> 14(4):413-428, figs. 1-7, annexe 1 & 2. [details] Available for editors
additional source Razouls, C. & C. Guinness. (1973). Variations saisonnières de la longueur et du volume chez Centropages typicus et Temora stylifera (Copepoda, Calanoidea) à Banyuls-sur-Mer (golfe du Lion). [Seasonal variations in length and volume in Centropages typicus and Temora stylifera (Copepoda, Calanoidea) in Banyuls-sur-Mer (Gulf of Lion).]. <em>Rapports et Procès-Verbaux des Réunions de la Commission Internationale pour l'Exploration Scientifique de la Mer Mediterranée, Monaco.</em> 21(8): 479-481. [details]
additional source Razouls, S. (1972). Variations annuelles du métabolisme respiratoire de deux Copépodes pélagiques: Temora stylifera et Centropages typicus à Banyuls-sur-Mer (golfe du Lion). [Annual variations in the respiratory metabolism of two pelagic copepods: Temora stylifera and Centropages typicus in Banyuls-sur-Mer (Gulf of Lion).]. <em>Vie et Milieu.</em> (A)22:95-112, figs. 1-7. (vi-1972). [details] Available for editors
additional source Razouls, S. (1973). Évolution des gonades chez les stades juvéniles d'un Copépode pélagique Temora stylifera (Calanoidea, Temoridae). [Evolution of gonads in juvenile stages of a pelagic copepod Temora stylifera (Calanoidea, Temoridae).]. <em>Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l'Académie des Sciences, Paris.</em> (D)277(15):1537-1539, pls. 1-2. (15-x-1973). [details]
additional source Razouls, S. (1975). Fécondité, maturité sexuelle et différenciation de l'appareil génital des femelles de deux Copépodes planctoniques: Centropages typicus et Temora stylifera. [Fecondity, sexual maturity and differentiation of the female genital tract of two planktonic copepods: Centropages typicus and Temora stylifera.]. <em>In: Bonaduce, G. & G.C. Carrada (eds.). Proceedings VIII. European marine Biology Symposium, Sorrento (Naples), 1973. Pubbl. Staz. zool. Napoli.</em> 39, suppl. 1:297-306, pls. 1-3, tabs. 1-2. (16-vi-1975). [details] Available for editors
additional source Razouls, S. & M. Apostolopoulou. (1978). Bilan énergétique de deux populations de Copépodes pélagiques Temora stylifera et Centropages typicus, en relation avec la présence d'une thermocline. [Energy balance of two populations of pelagic copepods Temora stylifera and Centropages typicus, in relation to the presence of a thermocline.]. <em>Vie et Milieu.</em> (B)27(1):13-25, figs. 1-2, tabs. 1-6. (iii-1978). [details] Available for editors
additional source Saiz, E. & M. Alcaraz. (1992). Free-swimming behaviour of Acartia clausi (Copepoda): Calanoida) under turbulent water movement. Marine Ecology Progress Series 80(2-3):229-236. [details] Available for editors
additional source Saudray, Y. & J.Y. Robert. (1971). Étude préliminaire du dimorphisme sexuel affectant l'antennule droite du mâle de Centrogages typicus Kröyer (Copepoda, Calanoida, Heterarthrandria) en microscope électronique à balayage. [Preliminary study of sexual dimorphism affecting the right antennule of the male of Centrogages typicus Kröyer (Copepoda, Calanoida, Heterarthrandria) in scanning electron microscopy.]. <em>Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l'Académie des Sciences, Paris.</em> (D)272: 1655-1657, fig. 1, pls. 1-2. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sciandra, A., J.L. Gouze & P. Nival. (1990). Modelling the reproduction of Centropages typicus (Copepoda: Calanoida) in a fluctuating food supply: effect of adaptation. <em>Journal of Plankton Research.</em> 12(3):549-572. [details] Available for editors
additional source Siokou-Frangou, I. (1985). Sur la présence du Copépode Calanoïde Pseudocalanus elongatus (Boeck) en mer égée du Nord. [On the presence of the Calanoid Copepod Pseudocalanus elongatus (Boeck) in the North Aegean Sea.]. <em>Rapports et Procès-Verbaux des Réunions de la Commission Internationale pour l'Exploration Scientifique de la Mer Mediterranée, Monaco.</em> 29(9): 231-233, fig. 1. (30-xii-1985, English and Greek summaries). [details]
additional source Smith, S.L. & P.V.Z. Lane. (1987). On the life history of Centropages typicus: responses to a fall diatom bloom in the New York Bight. Marine Biology, Berlin 95(2):305-313. [details] Available for editors
additional source Smith, S.L. & P.V.Z. Lane. (1988). Grazing of the spring diatom bloom in the New York Bight by the calanoid copepods Calanus finmarchicus, Metridia lucens, and Centropages typicus. Continental Shelf Research 8(5-7):485-510. [details] Available for editors
additional source Tomasini, J.A. & J. Mazza. (1979). Comportement alimentaire de Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida) en milieux nutritifs à deux algues et en présence de nauplii d'Artemia sp. [Feeding behavior of Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida) in nutrient media with two algae and in the presence of Artemia sp. nauplii.]. <em>Journal du Conseil International pour l'Exploration de la Mer.</em> 38(3):293-307, figs. 1-3, tabs. 1-8. (viii-1979). [details] Available for editors
additional source Vianello, G. (1968). Ricerche biometriche sue due popolazioni di Centropages typicus. [Biometric research on two populations of Centropages typicus.]. <em>Bollettino della Società Adriatica di Scienze Naturali in Trieste.</em> 56(1): 73-89, figs. 1-8. [details] Available for editors
additional source Wiadnyana, N.N. & F. Rassoulzadegan. (1989). Selective feeding of Acartia clausi and Centropages typicus on microzooplankton. Marine Ecology Progress Series 53(1):37-45. [details] Available for editors
additional source Suárez-Morales, E., J.W. Fleeger & P.A. Montagna. (2009). Free-living Copepoda (Crustacea) of the Gulf of Mexico. <em>In: Felder, D. L. & D.K. Camp [Eds]. Gulf of Mexico: origin, waters, and biota. Volume 1, Biodiversity. Texas A&M University Press, 1393 pp.</em> Chapter pagination: 841-869. [details] Available for editors
additional source Castellani, C., A.J. Lindley, M. Wootton, C.M. Lee & R.R. Kirby. (2012). Morphological and genetic variation in the North Atlantic copepod, Centropages typicus. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 92(1):99-106. [details] Available for editors
additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source ICES Zooplankton: Copepoda. sheet n° 32. [details]
additional source Bonnet, D., R.P. Harris, A. Lopez-Urrutia, C.Halsband-Lenk, W. Greve, L. Valdes, H.J. Hirche, M. Engel, M.T. Alvarez-Ossorio & K. Wiltshire. (2007). Comparative seasonal dynamics of Centropages typicus at seven coastal monitoring stations in the North Sea, English Channel and Bay of Biscay. <em>In: Carlotti, F. & R. Harris (eds.). The Biology of Centropages typicus. Progress in Oceanography.</em> 72(2-3):233-248. [details] Available for editors
additional source Wilson, C.B. (1932). The copepods of the Woods Hole region, Massachusetts. <em>Bulletin of the United States National Museum.</em> 158:1-635, figs. 1-316, pls. 1-41. [details] Available for editors
additional source Lawson, T.J. (1969). Centropages typical Krøyer, 1847 (Copepoda: Calanoida), its developmental stages and factors affecting its distribution. <em>M.S. Thesis, University of North Carolina.</em> 41 pp. [details] Available for editors
additional source Durbin, E. & J. Kane. (2007). Seasonal and spatial dynamics of Centropages typicus and C. hamatus in the western North Atlantic. <em>In: Carlotti, F. & R. Harris (eds.). The Biology of Centropages typicus. Progress in Oceanography.</em> 72(2-3):249-258. [details] Available for editors
additional source Paulmier, G. (2016). Les Copépodes (Crustacea, Calanoida) des eaux côtières et estuariennes de la Bretagne et de la Normandie. Section des Heterarthrandria. Copepoda (Crustacea, Calanoida) from coastal and estuaries waters of the Brittany and Normandy, Section Heterarthrandria. <em>Bulletin de la Societe Linneenne de Bordeaux.</em> 151, n.ser. 44(2/3):317-335. [details] Available for editors
additional source Lee, C.M. (1971). Population structures of the Planktonic Copepods Centropages typicus and Temora longicornis in the North Atlantic area and the functional significance of the reproductive structures of the Centropagidae. <em>PhD Thesis, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK.</em> 221 pp., available online at http://hdl.handle.net/1842/15198 [details] Available for editors
additional source Traboni, C., D. Sarno, M.R. d'Alcala & M.G. Mazzocch. (2023). Microplastics in the menu of Mediterranean zooplankton: Insights from the feeding response of the calanoid copepod Centropages typicus. <em>Marine Ecology - An Evolutionary Perspective.</em> 44(4):1-14. e12760. Jul 2023., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/eff.12737 [details] Available for editors
ecology source Brun, P., M.R. Payne & T. Kiørboe. (2017). A trait database for marine copepods. <em>Earth System Science Data.</em> 9(1):99-113., available online at https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-9-99-2017 [details] Available for editors
page(s): 603 [details]
context source (Deepsea) Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO. The Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS), available online at http://www.iobis.org/ [details]
context source (BeRMS 2020) Bio-environmental research group; Institute of Agricultural and Fisheries research (ILVO), Belgium; (2015): Zooplankton monitoring in the Belgian Part of the North Sea between 2009 and 2010. [details]
basis of record Boxshall, G. (2001). Copepoda (excl. Harpacticoida), <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 252-268 (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Brunel, P., L. Bosse & G. Lamarche. (1998). Catalogue of the marine invertebrates of the estuary and Gulf of St. Lawrence. <em>Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 126.</em> 405 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Roff, J.C. (1978). A guide to the marine flora and fauna of the Bay of Fundy: Copepoda: Calanoida. Fisheries and Marine Service Technical Report 823. 27 p. [details] Available for editors
additional source Muller, Y. (2004). Faune et flore du littoral du Nord, du Pas-de-Calais et de la Belgique: inventaire. [Coastal fauna and flora of the Nord, Pas-de-Calais and Belgium: inventory]. <em>Commission Régionale de Biologie Région Nord Pas-de-Calais: France.</em> 307 pp., available online at http://www.vliz.be/imisdocs/publications/145561.pdf [details]
additional source Arnaud, J., M. Brunet & J. Mazza. (1978). Studies on the midgut of Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida). <em>Cell and Tissue Research.</em> 187(2): 333-353, figs. 1-23, tabs. 1-2. [details] Available for editors
additional source Arnaud, J., M. Brunet & J. Mazza. (1987). Rôle des cellules B de l'intestin moyen chez Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida). [Role of midgut B cells in Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida).]. <em>Réproduction, Nutrition, et Développement.</em> 27(4): 817-827. [details] Available for editors
additional source Arnaud, J., M. Brunet & J. Mazza. (1988). Labral glands in Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida). I. Sites of synthesis. <em>Journal of Morphology.</em> 197(1): 21-32. [details] Available for editors
additional source Blades, P.I. (1977). Mating behavior of Centropages typicus (Copepoda: Calanoida). Marine Biology, Berlin 40(1):57-64, figs. 1-7. (25-ii-1977) [details] Available for editors
additional source Caparroy, P., M.T. Perez & F. Carlotti. (1998). Feeding behaviour of Centropages typicus in calm and turbulent conditions. Marine Ecology Progress Series 168:109-118. (9.vii.1998) [details] Available for editors
additional source Carlton, J.T. & J.B. Geller. (1993). Ecological roulette: the global transport of nonindigenous marine organisms. Science, New York 261:78-82. [details] Available for editors
additional source Cowles, T.J. & J.R. Strickler. (1983). Characterization of feeding activity patterns in the planktonic copepod Centropages typicus Kroyer under various food conditions. Limnology and Oceanography 28(1):106-115, figs. 1-11, tabs. 1-2. (i-1983) [details] Available for editors
additional source Dagg, M.J. (1978). Estimated, in situ, rates of egg production for the copepod Centropages typicus (Kroyer) in the New York bight. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 34(3):183-196, figs. 1-9, tab. 1. [details] Available for editors
additional source Dagg, M.J. & D.W. Grill. (1980). Natural feeding rates of Centropages typicus females in the New York Bight. Limnology and Oceanography 25(4):597-609, figs. 1-6, tabs. 1-2. (vii-1980) [details] Available for editors
additional source Grandori, R. (1925). Sulle sviluppo larvale di Centropages typicus Kroyer. [On the larval development of Centropages typicus Kroyer.]. <em>Rivista di Biologia.</em> 7:137-145, figs. 1-10. [details] Available for editors
additional source Gaudy, R. (1971). Étude expérimentale de la ponte chez trois espèces de Copépodes pélagiques (Centropages typicus, Acartia clausi et Temora stylifera). [Experimental study of spawning in three species of pelagic copepods (Centropages typicus, Acartia clausi and Temora stylifera).]. <em>Marine Biology, Berlin.</em> 9(1): 65-70, fig. 1, tab. 1. [details] Available for editors
additional source Gaudy, R. (1971). L'allongement antennulaire chez <i>Centropages typicus</i>, signification adaptative et utilité biométrique. [Antennular elongation in <i>Centropages typicus</i>, adaptive significance and biometric utility. <em>Rapports et Procès-Verbaux des Réunions de la Commission Internationale pour l'Exploration Scientifique de la Mer Mediterranée, Monaco.</em> 20(3): 363-365, fig. 1. [details] Available for editors
additional source Ianora, A. (1990). The effect of reproductive condition on egg production rates in the planktonic copepod Centropages typicus. Journal of Plankton Research 12(4):885-890. [details] Available for editors
additional source Grant, G.C. (1988). Seasonal occurrence and dominance of Centropages congeners in the Middle Atlantic Bight, USA. <em>In: Boxshall, G.A. & H.K. Schminke (eds.). Biology of Copepods. Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Copepoda. Developments in Hydrobiolology 47, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Hydrobiologia.</em> 47(167/168):227-237, figs. 1-3, tabs. 1-5. [details] Available for editors
additional source Guerrero, F., S. Nival & P. Nival. (1997). Egg production and viability in Centropages typicus: A laboratory study on the effect of food concentration. <em>Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom.</em> 77(1):257-260. [details] Available for editors
additional source Johnson, W.H. & J.E.G. Raymond. (1939). The reactions of the planktonic copepod, Centropages typicus, to light and gravity. Biological Bulletin, Woods Hole 77(2):200-215, tabs. 1-5. (x-1939) [details] Available for editors
additional source Ianora, A. & I. Buttino. (1990). Seasonal cycles in population abundances and egg production rates in the planktonic copepods Centropages typicus and Acartia clausi. Journal of Plankton Research 12(3):473-481. [details] Available for editors
additional source Ianora, A., A. Miralto & S. Vanucci. (1992). The surface attachment structure: a unique type of integumental formation in neustonic copepods. <em>Marine Biology, Berlin.</em> 113(3):401-407, figs. 1-5. [details] Available for editors
additional source Lawson, T.J. & G.D. Grice. (1970). The developmental stages of Centropages typicus Kroyer (Copepoda, Calanoida). Crustaceana, Leiden 18(2):187-208, figs. 1-137. (25-iii-1970) [details] Available for editors
additional source Lee, C.M. (1972). Structure and function of the spermatophore and its coupling device in the Centropagidae (Copepoda: Calanoida). Bulletin of Marine Ecology 8(1):1-20, figs. 1-10, pls. 1-10, tabs. 1-2. (ix-1972) [details] Available for editors
additional source Linko, A.K. (1907). Untersuchungen über das Plankton des Barents Meeres. [Investigations on the plankton of the Barents Sea.]. <em>Wissenschaftlich praktische Murman Expedition, St. Petersburg.</em> :1-247, figs.1-21. [details]
additional source McAden, D.C., G.N. Greene & W.B. Baker, Jr. (1987). First record of Centropages typicus Kroyer (Copepoda: Centropagidae) in the Gulf of Mexico. Texas Journal of Science 39(3):290-291. [details] Available for editors
additional source Muxagata, E.M. & J.A. Williams. (2004). The Mesozooplankton of the Solent-Southampton Water system: a photographic guide. Southampton Oceanography Centre, Southampton, U.K. 103 pp. [details] Available for editors
additional source Nival, S., M. Pagano & P. Nival. (1990). Laboratory study of the spawning rate of the calanoid copepods Centropages typicus: effect of fluctuating food concentration. Journal of Plankton Research 12(3):535-547. [details] Available for editors
additional source Pesta, O. (1928). Krebstiere oder Crustacea. I: Ruderfüsser oder Copepoda (1. Calanoida, 2. Cyclopoida) (3. Ordnung) [Crustaceans or Crustacea. I: Copepods (1. Calanoida, 2. Cyclopoida) (3rd order).]. <em>In: Dahl, F. (ed.). Die Tierwelt Deutschlands und der Angrenzenden Meeresteile nach Ihren Merkmalen und nach Ihrer Lebensweise. Fischer, Jena.</em> 9:1-136, figs. 1-115. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sars, G.O. (1902). Copepoda Calanoida, Parts VII & VIII, Centropagidae, Diaptomidae. <em>An Account of the Crustacea of Norway, with short descriptions and figures of all the species. Bergen Museum.</em> 4:73-96, pls. 49-64. [details]
additional source Razouls, C. (1973). Variations annuelles quantitatives de deux espèces dominantes de Copépodes planctoniques Centropages typicus et Temora stylifera de la région de Banyuls: Cycles biologiques et estimations de la production. I. Méthodologie et mise en évidence de l'importance quantitative de ces deux espèces par rapport à l'ensemble des Copépodes. [Annual quantitative variations of two dominant species of planktonic copepods Centropages typicus and Temora stylifera from the Banyuls region: Biological cycles and production estimates. I. Methodology and highlighting of the quantitative importance of these two species in relation to all copepods.]. <em>Cahiers de Biologie Marine.</em> 14(3):361-390, tabs. 1-11, annexe 1 & 2. [details] Available for editors
additional source Razouls, C. (1974). Variations annuelles quantitatives de deux espèces dominantes de Copépodes planctoniques Centropages typicus et Temora stylifera de la région de Banyuls: cycles biologiques et estimations de la production. III. Dynamique des populations et calcul de leur production. [Annual quantitative variations of two dominant species of planktonic copepods Centropages typicus and Temora stylifera from the Banyuls region: biological cycles and production estimates. III. Population dynamics and calculation of their production.]. <em>Cahiers de Biologie Marine.</em> 15(1):51-88, figs. 1-9, tabs. 1-4, annexe I & II. (15-ii-1974). [details] Available for editors
additional source Razouls, C. & C. Guinness. (1973). Variations annuelles quantitatives de deux espèces dominantes de Copépodes planctoniques Centropages typicus et Temora stylifera de la région de Banyuls: cycles biologiques et estimation de la production. II. Variations dimensionales et mesures de la croissance. [Annual quantitative variations of two dominant species of planktonic copepods Centropages typicus and Temora stylifera from the Banyuls region: biological cycles and production estimation. II. Dimensional variations and growth measurements.]. <em>Cahiers de Biologie Marine.</em> 14(4):413-428, figs. 1-7, annexe 1 & 2. [details] Available for editors
additional source Razouls, C. & C. Guinness. (1973). Variations saisonnières de la longueur et du volume chez Centropages typicus et Temora stylifera (Copepoda, Calanoidea) à Banyuls-sur-Mer (golfe du Lion). [Seasonal variations in length and volume in Centropages typicus and Temora stylifera (Copepoda, Calanoidea) in Banyuls-sur-Mer (Gulf of Lion).]. <em>Rapports et Procès-Verbaux des Réunions de la Commission Internationale pour l'Exploration Scientifique de la Mer Mediterranée, Monaco.</em> 21(8): 479-481. [details]
additional source Razouls, S. (1972). Variations annuelles du métabolisme respiratoire de deux Copépodes pélagiques: Temora stylifera et Centropages typicus à Banyuls-sur-Mer (golfe du Lion). [Annual variations in the respiratory metabolism of two pelagic copepods: Temora stylifera and Centropages typicus in Banyuls-sur-Mer (Gulf of Lion).]. <em>Vie et Milieu.</em> (A)22:95-112, figs. 1-7. (vi-1972). [details] Available for editors
additional source Razouls, S. (1973). Évolution des gonades chez les stades juvéniles d'un Copépode pélagique Temora stylifera (Calanoidea, Temoridae). [Evolution of gonads in juvenile stages of a pelagic copepod Temora stylifera (Calanoidea, Temoridae).]. <em>Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l'Académie des Sciences, Paris.</em> (D)277(15):1537-1539, pls. 1-2. (15-x-1973). [details]
additional source Razouls, S. (1975). Fécondité, maturité sexuelle et différenciation de l'appareil génital des femelles de deux Copépodes planctoniques: Centropages typicus et Temora stylifera. [Fecondity, sexual maturity and differentiation of the female genital tract of two planktonic copepods: Centropages typicus and Temora stylifera.]. <em>In: Bonaduce, G. & G.C. Carrada (eds.). Proceedings VIII. European marine Biology Symposium, Sorrento (Naples), 1973. Pubbl. Staz. zool. Napoli.</em> 39, suppl. 1:297-306, pls. 1-3, tabs. 1-2. (16-vi-1975). [details] Available for editors
additional source Razouls, S. & M. Apostolopoulou. (1978). Bilan énergétique de deux populations de Copépodes pélagiques Temora stylifera et Centropages typicus, en relation avec la présence d'une thermocline. [Energy balance of two populations of pelagic copepods Temora stylifera and Centropages typicus, in relation to the presence of a thermocline.]. <em>Vie et Milieu.</em> (B)27(1):13-25, figs. 1-2, tabs. 1-6. (iii-1978). [details] Available for editors
additional source Saiz, E. & M. Alcaraz. (1992). Free-swimming behaviour of Acartia clausi (Copepoda): Calanoida) under turbulent water movement. Marine Ecology Progress Series 80(2-3):229-236. [details] Available for editors
additional source Saudray, Y. & J.Y. Robert. (1971). Étude préliminaire du dimorphisme sexuel affectant l'antennule droite du mâle de Centrogages typicus Kröyer (Copepoda, Calanoida, Heterarthrandria) en microscope électronique à balayage. [Preliminary study of sexual dimorphism affecting the right antennule of the male of Centrogages typicus Kröyer (Copepoda, Calanoida, Heterarthrandria) in scanning electron microscopy.]. <em>Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Séances de l'Académie des Sciences, Paris.</em> (D)272: 1655-1657, fig. 1, pls. 1-2. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sciandra, A., J.L. Gouze & P. Nival. (1990). Modelling the reproduction of Centropages typicus (Copepoda: Calanoida) in a fluctuating food supply: effect of adaptation. <em>Journal of Plankton Research.</em> 12(3):549-572. [details] Available for editors
additional source Siokou-Frangou, I. (1985). Sur la présence du Copépode Calanoïde Pseudocalanus elongatus (Boeck) en mer égée du Nord. [On the presence of the Calanoid Copepod Pseudocalanus elongatus (Boeck) in the North Aegean Sea.]. <em>Rapports et Procès-Verbaux des Réunions de la Commission Internationale pour l'Exploration Scientifique de la Mer Mediterranée, Monaco.</em> 29(9): 231-233, fig. 1. (30-xii-1985, English and Greek summaries). [details]
additional source Smith, S.L. & P.V.Z. Lane. (1987). On the life history of Centropages typicus: responses to a fall diatom bloom in the New York Bight. Marine Biology, Berlin 95(2):305-313. [details] Available for editors
additional source Smith, S.L. & P.V.Z. Lane. (1988). Grazing of the spring diatom bloom in the New York Bight by the calanoid copepods Calanus finmarchicus, Metridia lucens, and Centropages typicus. Continental Shelf Research 8(5-7):485-510. [details] Available for editors
additional source Tomasini, J.A. & J. Mazza. (1979). Comportement alimentaire de Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida) en milieux nutritifs à deux algues et en présence de nauplii d'Artemia sp. [Feeding behavior of Centropages typicus (Copepoda, Calanoida) in nutrient media with two algae and in the presence of Artemia sp. nauplii.]. <em>Journal du Conseil International pour l'Exploration de la Mer.</em> 38(3):293-307, figs. 1-3, tabs. 1-8. (viii-1979). [details] Available for editors
additional source Vianello, G. (1968). Ricerche biometriche sue due popolazioni di Centropages typicus. [Biometric research on two populations of Centropages typicus.]. <em>Bollettino della Società Adriatica di Scienze Naturali in Trieste.</em> 56(1): 73-89, figs. 1-8. [details] Available for editors
additional source Wiadnyana, N.N. & F. Rassoulzadegan. (1989). Selective feeding of Acartia clausi and Centropages typicus on microzooplankton. Marine Ecology Progress Series 53(1):37-45. [details] Available for editors
additional source Suárez-Morales, E., J.W. Fleeger & P.A. Montagna. (2009). Free-living Copepoda (Crustacea) of the Gulf of Mexico. <em>In: Felder, D. L. & D.K. Camp [Eds]. Gulf of Mexico: origin, waters, and biota. Volume 1, Biodiversity. Texas A&M University Press, 1393 pp.</em> Chapter pagination: 841-869. [details] Available for editors
additional source Castellani, C., A.J. Lindley, M. Wootton, C.M. Lee & R.R. Kirby. (2012). Morphological and genetic variation in the North Atlantic copepod, Centropages typicus. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 92(1):99-106. [details] Available for editors
additional source Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). , available online at http://www.itis.gov [details]
additional source ICES Zooplankton: Copepoda. sheet n° 32. [details]
additional source Bonnet, D., R.P. Harris, A. Lopez-Urrutia, C.Halsband-Lenk, W. Greve, L. Valdes, H.J. Hirche, M. Engel, M.T. Alvarez-Ossorio & K. Wiltshire. (2007). Comparative seasonal dynamics of Centropages typicus at seven coastal monitoring stations in the North Sea, English Channel and Bay of Biscay. <em>In: Carlotti, F. & R. Harris (eds.). The Biology of Centropages typicus. Progress in Oceanography.</em> 72(2-3):233-248. [details] Available for editors
additional source Wilson, C.B. (1932). The copepods of the Woods Hole region, Massachusetts. <em>Bulletin of the United States National Museum.</em> 158:1-635, figs. 1-316, pls. 1-41. [details] Available for editors
additional source Lawson, T.J. (1969). Centropages typical Krøyer, 1847 (Copepoda: Calanoida), its developmental stages and factors affecting its distribution. <em>M.S. Thesis, University of North Carolina.</em> 41 pp. [details] Available for editors
additional source Durbin, E. & J. Kane. (2007). Seasonal and spatial dynamics of Centropages typicus and C. hamatus in the western North Atlantic. <em>In: Carlotti, F. & R. Harris (eds.). The Biology of Centropages typicus. Progress in Oceanography.</em> 72(2-3):249-258. [details] Available for editors
additional source Paulmier, G. (2016). Les Copépodes (Crustacea, Calanoida) des eaux côtières et estuariennes de la Bretagne et de la Normandie. Section des Heterarthrandria. Copepoda (Crustacea, Calanoida) from coastal and estuaries waters of the Brittany and Normandy, Section Heterarthrandria. <em>Bulletin de la Societe Linneenne de Bordeaux.</em> 151, n.ser. 44(2/3):317-335. [details] Available for editors
additional source Lee, C.M. (1971). Population structures of the Planktonic Copepods Centropages typicus and Temora longicornis in the North Atlantic area and the functional significance of the reproductive structures of the Centropagidae. <em>PhD Thesis, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK.</em> 221 pp., available online at http://hdl.handle.net/1842/15198 [details] Available for editors
additional source Traboni, C., D. Sarno, M.R. d'Alcala & M.G. Mazzocch. (2023). Microplastics in the menu of Mediterranean zooplankton: Insights from the feeding response of the calanoid copepod Centropages typicus. <em>Marine Ecology - An Evolutionary Perspective.</em> 44(4):1-14. e12760. Jul 2023., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/eff.12737 [details] Available for editors
ecology source Brun, P., M.R. Payne & T. Kiørboe. (2017). A trait database for marine copepods. <em>Earth System Science Data.</em> 9(1):99-113., available online at https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-9-99-2017 [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
Marine Planktonic Copepods (Banyuls/OOB/UPMC/CNRS) Note: Including taxonomic identification plates, remarks, geographic distribution, ecological information & reference list
PlanktonNet Image
To Barcode of Life (144 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (150 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Centropages typicus)
To GenBank (148 nucleotides; 138 proteins)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (81 records)
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 033845)
To ITIS
PlanktonNet Image
To Barcode of Life (144 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (150 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Centropages typicus)
To GenBank (148 nucleotides; 138 proteins)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (81 records)
To Yale Peabody Museum of Natural History (YPM IZ 033845)
To ITIS